Documents
Poster
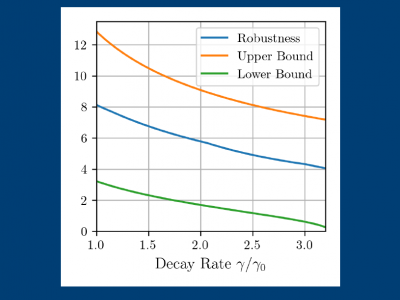
Exact classification of NMR spectra from NMR signals
- DOI:
- 10.60864/rr1y-6f09
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Carlos Sing Long
- Last updated:
- 11 April 2024 - 11:00am
- Document Type:
- Poster
- Document Year:
- 2024
- Event:
- Presenters:
- Pedro Izquierdo Lehmann, Carlos Sing Long
- Paper Code:
- SPTM-P2.8
- Categories:
- Log in to post comments
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is routinely used to study the properties of matter. Therefore, different materials can be classified according to their NMR spectra. However, the NMR spectra cannot be observed directly, and only the NMR signal, which is a sum of complex exponentials, is directly observable in practice. A popular approach to recover the spectrum is to perform harmonic retrieval, i.e., to reconstruct exactly the spectrum from the NMR signal. However, even when this approach fails, the spectrum might still be classified accurately. In this work, we model the spectrum as an atomic measure to study the performance of classifying the spectrum from the NMR signal, and to determine how it degrades in the presence of additive noise and changes in field intensity. Although we focus on NMR signals, our results are broadly applicable to sum-of-exponential signals. We show numerical results illustrating our claims.

