
ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2017 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics. Visit ICASSP 2017
- Read more about A Scalable Convolutional Neural Network for Task-specified Scenarios via Knowledge Distillation
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we explore the redundancy in convolutional neural network, which scales with the complexity of vision tasks. Considering that many front-end visual systems are interested in only a limited range of visual targets, the removing of task-specified network redundancy can promote a wide range of potential applications. We propose a task-specified knowledge distillation algorithm to derive a simplified model with pre-set computation cost and minimized accuracy loss, which suits the resource constraint front-end systems well.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about Atomic Norm Minimization for Modal Analysis with Random Spatial Compression
- Log in to post comments
Identifying characteristic vibrational modes and frequencies is of great importance for monitoring the health of structures such as buildings and bridges. In this work, we address the problem of estimating the modal parameters of a structure from small amounts of vibrational data collected from wireless sensors distributed on the structure. We consider a randomized spatial compression scheme for minimizing the amount of data that is collected and transmitted by the sensors.
ICASSP2017.pdf
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views- Read more about Facial Attractiveness Prediction Using Psychologically Inspired Convolutional Neural Network (PI-CNN)
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a psychologically inspired convolutional neural network (PI-CNN) to achieve automatic facial beauty prediction. Different from the previous methods, the PI-CNN is a hierarchical model that facilitates both the facial beauty representation learning and predictor training. Inspired by the recent psychological studies, significant appearance features of facial detail, lighting and color were used to optimize the PI-CNN facial beauty predictor using a new cascaded fine-tuning method.
- Categories:
 64 Views
64 ViewsRecently, multidimensional signal reconstruction using a low number of measurements is of great interest. Therefore, an effective sampling scheme which should acquire the most information of signal using a low number of measurements is required. In this paper, we study a novel cube-based method for sampling and reconstruction of multidimensional signals. First, inspired by the block-based compressive sensing (BCS), we divide a group of pictures (GoP) in a video sequence into cubes. By this way, we can easily store the measurement matrix and also easily can generate the sparsifying basis.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 137 Views
137 Views
- Read more about Active Speech Control using Wave-Domain Processing with a Linear Wall of Dipole Secondary Sources
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we investigate the effects of compensating for wave-domain filtering delay in an active speech control system. An active control system utilising wave-domain processed basis functions is evaluated for a linear array of dipole secondary sources. The target control soundfield is matched in a least squares sense using orthogonal wavefields to a predicted future target soundfield. Filtering is implemented using a block-based short-time signal processing approach which induces an inherent delay.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views- Read more about Dual-Fisheye Lens Stiching for 360-Degree Imaging
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about I-VECTOR/PLDA SPEAKER RECOGNITION USING SUPPORT VECTORS WITH DISCRIMINANT ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
i-Vector feature representation with probabilistic linear discriminant analysis (PLDA) scoring in speaker recognition system has recently achieved effective performance even on channel mismatch conditions. In general, experiments carried out using this combined strategy employ linear discriminant analysis (LDA) after the i-Vector extraction phase to suppress irrelevant directions, such as those introduced by noise or channel distortions. However, speaker-related and -non-related variability present in the data may prevent LDA from finding the best projection matrix.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Robust Particle Filter by Dynamic Averaging of Multiple Noise Models
- Log in to post comments
State filtering is a key problem in many signal processing applications. From a series of noisy measurement, one would like to estimate the state of some dynamic system. Existing techniques usually adopt a Gaussian noise assumption which may result in a major degradation in performance when the measurements are with the presence of outliers. A robust algorithm immune to the presence of outliers is desirable.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views- Read more about Jointly Optimized Transform Domain Temporal Prediction and Sub-pixel Interpolation
- Log in to post comments
Conventional pixel-domain block matching temporal (inter) prediction is suboptimal, since it ignores the underlying spatial correlation. Hence in our recent research we proposed transform domain temporal prediction (TDTP), wherein spatially de-correlated transform coefficients are individually predicted. Later we proposed extended block TDTP (EB-TDTP), which fully exploits spatial correlation around reference block boundaries. However, the transform domain temporal correlation exploited by (EB-)TDTP interferes with the frequency response of sub-pixel interpolation filters.
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views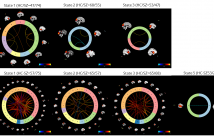
- Read more about Identifying fMRI Dynamic Connectivity States Using Affinity Propagation Clustering Method: Application to Schizophrenia
- Log in to post comments
Numerous studies have shown that brain functional connectivity patterns can be time-varying over periods of tens of seconds. K-means has been widely used to extract the connectivity states from dynamic functional connectivity. However, K-means is dependent on initialization and can be exponentially slow in converging due to extensive noise in dynamic functional connectivity. In this work, we propose to use an affinity propagation clustering method to estimate the connectivity states. The new approach found more meaningful group differences than K-means. Our finding supports that our method is promising in exploring biomarkers of mental disorders.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views