
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about DNN BASED EMBEDDINGS FOR LANGUAGE RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we present a language identification (LID) system based on embeddings. In our case, an embedding is a fixed-length vector (similar to i-vector) that represents the whole utterance, but unlike i-vector it is designed to contain mostly information relevant to the target task (LID). In order to obtain these embeddings, we train a deep neural network (DNN) with sequence summarization layer to classify languages.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about FLEXIBLE MULTI-GROUP SINGLE CARRIER MODULATION: OPTIMAL SUBCARRIER GROUPING AND RATE MAXIMIZATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views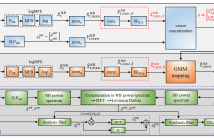
- Read more about EXPLOITING EXPLICIT MEMORY INCLUSION FOR ARTIFICIAL BANDWIDTH EXTENSION
- Log in to post comments
Artificial bandwidth extension (ABE) algorithms have been developed to improve speech quality when wideband devices are used in conjunction with narrowband devices or infrastructure. While past work points to the benefit of using contextual information or memory for ABE, an understanding of the relative benefit of explicit memory inclusion, rather than just dynamic information, calls for a comparative, quantitative analysis. The need for practical ABE solutions calls further for the inclusion of memory without significant increases to latency or computational complexity.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about EFFICACY OF MULTIUSER MASSIVE MISO WIRELESS ENERGY TRANSFER UNDER IQ IMBALANCE AND CHANNEL ESTIMATION ERRORS OVER RICIAN FADING
- Log in to post comments
We investigate the practical realization of energy beamforming gains in the downlink wireless power transfer from a massive antenna radio frequency (RF) source to multiple single antenna energy harvesting (EH) users. Assuming channel reciprocity for the uplink and downlink channels undergoing Rician fading, we first obtain the least-squares and linear-minimum-mean-square-error channel estimates using the energy-constrained pilot signal transmission from EH users.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
Millimeter wave (mmWave) multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) transceivers employ narrow beams to obtain a large array-gain, rendering them sensitive to changes in the angles of arrival and departure of the paths. Since the singular vectors that span the channel subspace are used to design the precoder and combiner, we propose a method to track the receiver-side channel subspace during data transmission using a separate radio frequency (RF) chain dedicated for channel tracking.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Deep Geometric Matrix Completion
- Log in to post comments
ICASSP.pdf
- Categories:
 104 Views
104 Views
- Read more about ROBUST OBJECT-AWARE SAMPLE CONSENSUS WITH APPLICATION TO LIDAR ODOMETRY
- Log in to post comments
Random sample consensus (RANSAC) is a popular paradigm for parameter estimation with outlier detection, which plays an essential role in 3D robot vision, especially for LiDAR odometry. The success of RANSAC strongly depends on the probability of selecting a subset of pure inliers, which sets barriers to robust and fast parameter estimation. Although significant efforts have been made to improve RANSAC in various scenarios, its strong dependency on inlier selection is still a problem.
海报0411晚修改.pdf
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about 3D IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION FROM MULTI-FOCUS MICROSCOPE: AXIAL SUPER-RESOLUTION AND MULTIPLE-FRAME PROCESSING
- Log in to post comments
ICASSP2018_mf_mfm.pdf
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about FAST AND ADAPTIVE BLIND AUDIO SOURCE SEPARATION USING RECURSIVE LEVENBERG-MARQUARDT SYNCHROSQUEEZING
- Log in to post comments
This paper revisits the Degenerate Unmixing Estimation Technique (DUET) for blind audio separation of an arbitrary
number of sources given two mixtures through a recursively computed and adaptive time-frequency representation.
Recently, synchrosqueezing was introduced as a promising signal disentangling method which allows to compute reversible
and sharpen time-frequency representations. Thus, it can be used to reduce overlaps between the sources in the
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about ANALYSIS OF MULTILINGUAL BLSTM ACOUSTIC MODEL ON AND HIGH RESOURCE LANGUAGES
- Log in to post comments
The paper provides an analysis of automatic speech recognition
systems (ASR) based on multilingual BLSTM, where we used multi-task
training with separate classification layer for each language. The
focus is on low resource languages, where only a limited
amount of transcribed speech is available. In such
scenario, we found it
essential to train the ASR systems in a multilingual fashion and we
report superior results
obtained with pre-trained multilingual BLSTM on this task.
The high resource languages are also
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views