
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.
- Read more about HAND GESTURE RECOGNITION USING A SKELETON-BASED FEATURE REPRESENTATION WITH A RANDOM REGRESSION FOREST
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a method for automatic hand gesture recognition using a random regression forest with a novel set of feature descriptors created from skeletal data acquired from the Leap Motion Controller. The efficacy of our proposed approach is evaluated on the publicly available University of Padova Microsoft Kinect and Leap Motion dataset, as well as 24 letters of the English alphabet in American Sign Language. The letters that are dynamic (e.g. j and z) are not evaluated.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about Combining Gaze and Demographic Feature Desciptors for Autism Classification
- Log in to post comments
People with autism suffer from social challenges and communication difficulties, which may prevent them from leading a fruitful and enjoyable life. It is imperative to diagnose and start treatments for autism as early as possible and, in order to do so, accurate methods of identifying the disorder are vital. We propose a novel method for classifying autism through the use of eye gaze and demographic feature descriptors that include a subject’s age and gender. We construct feature descriptors that incorporate the subject’s age and gender, as well as features based on eye gaze data.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 ViewsVoxels are an effective approach to 3D mesh and point cloud classification because they build upon mature Convolutional Neural Network concepts. We show however that their cubic increase in dimensionality is unsuitable for more challenging problems such as object detection in a complex point cloud scene. We observe that 3D meshes are analogous to graph data and can thus be treated with graph signal processing techniques.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views- Read more about Presentation Slides for paper #3118
- Log in to post comments
Gradient control plays an important role in feed-forward networks applied to various computer vision tasks. Previous work has shown that Recurrent Highway Networks minimize the problem of vanishing or exploding gradients. They achieve this by setting the eigenvalues of the temporal Jacobian to 1 across the time steps. In this work, batch normalized recurrent highway networks are proposed to control the gradient flow in an improved way for network convergence. Specifically, the introduced model can be formed by batch normalizing the inputs at each recurrence loop.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 ViewsThe capability of determining the quality of target detections is important for applications using smart cameras, such as autonomous robotics and surveillance. We propose to estimate the quality of target detections by integrating the target location uncertainty over polygonal domains, which represent the fields of view of the cameras. We define a framework based on numerical integration that easily accommodates multiple models for uncertainty and fields of view.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about SCALABLE LIGHT FIELD COMPRESSION SCHEME USING SPARSE RECONSTRUCTION AND RESTORATION
- Log in to post comments
This poster describes a light field scalable compression scheme based on the sparsity of the angular Fourier transform of the light field. A subset of sub-aperture images (or views) is compressed using HEVC as a base layer and transmitted to the decoder. An entire light field is reconstructed from this view subset using a method exploiting the sparsity of the light field in the continuous Fourier domain. The reconstructed light field is enhanced using a patch-based restoration method. Then, restored samples are used to predict original ones, in a SHVC-based SNR-scalable scheme.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views- Read more about Adaptive thresholding HOSVD algorithm with iterative regularization for image denoising
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views- Read more about Adaptive thresholding HOSVD algorithm with iterative regularization for image denoising
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about ICIP 2017 - SPS Welcoming Remarks, Rabab Ward, IEEE SPS President
- Log in to post comments
IEEE Signal Processing Society welcoming remarks slides from IEEE President, Rabab Ward at ICIP 2017 on 18 September 2017 in Beijing, China.
Accompanying video can be fount on the Resource Center as well as IEEE SPS YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NRRzs0bB0a0.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views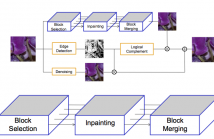
- Read more about INPAINTING-BASED CAMERA ANONYMIZATION
- Log in to post comments
Over the years, the forensic community has developed a series of very accurate camera attribution algorithms enabling to detect which device has been used to acquire an image with outstanding results. Many of these methods are based on photo response non uniformity (PRNU) that allows tracing back a picture to the camera used to shoot it. However, when privacy is required, it would be desirable to anonymize photos, unlinking them from their specific device. This paper investigates a new and alternative approach to image anonymization task.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views