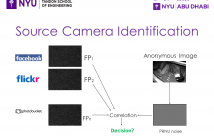
PRNU (Photo Response Non-Uniformity)-based camera fingerprints are useful for identifying the source camera of an anonymous image. As the query image has to be correlated with each candidate camera fingerprint, one key concern of this approach is the high run time overhead when using a large camera database. Clever techniques have been proposed to reduce the computation and I/O time either by reducing the size of the fingerprint or by group testing where multiple candidate fingerprints can be eliminated by a single correlation operation.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
PRNU (Photo Response Non-Uniformity)-based camera fingerprints are useful for identifying the source camera of an anonymous image. As the query image has to be correlated with each candidate camera fingerprint, one key concern of this approach is the high run time overhead when using a large camera database. Clever techniques have been proposed to reduce the computation and I/O time either by reducing the size of the fingerprint or by group testing where multiple candidate fingerprints can be eliminated by a single correlation operation.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
PRNU (Photo Response Non-Uniformity)-based camera fingerprints are useful for identifying the source camera of an anonymous image. As the query image has to be correlated with each candidate camera fingerprint, one key concern of this approach is the high run time overhead when using a large camera database. Clever techniques have been proposed to reduce the computation and I/O time either by reducing the size of the fingerprint or by group testing where multiple candidate fingerprints can be eliminated by a single correlation operation.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
PRNU (Photo Response Non-Uniformity)-based camera fingerprints are useful for identifying the source camera of an anonymous image. As the query image has to be correlated with each candidate camera fingerprint, one key concern of this approach is the high run time overhead when using a large camera database. Clever techniques have been proposed to reduce the computation and I/O time either by reducing the size of the fingerprint or by group testing where multiple candidate fingerprints can be eliminated by a single correlation operation.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views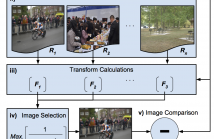
- Read more about Spotting the Difference: Context Retrieval and Analysis for Improved Forgery Detection and Localization
- Log in to post comments
As image tampering becomes ever more sophisticated and commonplace, the need for image forensics algorithms that can accurately and quickly detect forgeries grows. In this paper, we revisit the ideas of image querying and retrieval to provide clues to better localize forgeries. We propose a method to perform large-scale image forensics on the order of one million images using the help of an image search algorithm and database to gather contextual clues as to where tampering may have taken place.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views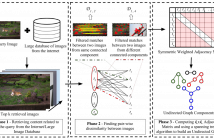
- Read more about U-Phylogeny: Undirected Provenance Graph Construction in the Wild
- Log in to post comments
Deriving relationships between images and tracing back their history of modifications are at the core of Multimedia Phylogeny solutions, which aim to combat misinformation through doctored visual media. Nonetheless, most recent image phylogeny solutions cannot properly address cases of forged composite images with multiple donors, an area known as multiple parenting phylogeny (MPP). This paper presents a preliminary undirected graph construction solution for MPP, without any strict assumptions.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views