- Transducers
- Spatial and Multichannel Audio
- Source Separation and Signal Enhancement
- Room Acoustics and Acoustic System Modeling
- Network Audio
- Audio for Multimedia
- Audio Processing Systems
- Audio Coding
- Audio Analysis and Synthesis
- Active Noise Control
- Auditory Modeling and Hearing Aids
- Bioacoustics and Medical Acoustics
- Music Signal Processing
- Loudspeaker and Microphone Array Signal Processing
- Echo Cancellation
- Content-Based Audio Processing
- Read more about Perceptually-motivated environment-specific speech enhancement
- Log in to post comments
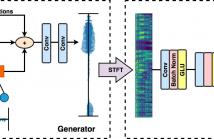
This paper introduces a deep learning approach to enhance speech recordings made in a specific environment. A single neural network learns to ameliorate several types of recording artifacts, including noise, reverberation, and non-linear equalization. The method relies on a new perceptual loss function that combines adversarial loss with spectrogram features. Both subjective and objective evaluations show that the proposed approach improves on state-of-the-art baseline methods.
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views
- Read more about SEQUENTIAL STRUCTURED DICTIONARY LEARNING FOR BLOCK SPARSE REPRESENTATIONS
- Log in to post comments
Dictionary learning algorithms have been successfully applied to a number of signal and image processing problems. In some applications however, the observed signals may have a multi-subpsace structure that enables block-sparse signal representations. Based on the observation that the observed signals can be approximated as a sum of low rank matrices, a new algorithm for learning a block-structured dictionary for block-sparse signal representations is proposed.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about DETECTING GAS VAPOR LEAKS THROUGH UNCALIBRATED SENSOR BASED CPS
- Log in to post comments
CPS comprised of ordinary people or first responders is proposed to detect gas vapor in open air.
This CPS will use low-cost sensors coupled to smart phones or mobile devices.
The efficacy of CPS hinges on its ability to address technical challenges stemming from the fact that sensors may produce different results under the same conditions due to sensor drift, noise, and/or resolution errors.
The proposed system makes use of time-varying signals produced by sensors to detect gas leaks. Sensors sample the gas vapor level in a continuous manner
icassp2019.pdf
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
This paper proposes an approach to the joint modeling of the short-time Fourier transform magnitude and phase spectrograms with a deep generative model. We assume that the magnitude follows a Gaussian distribution and the phase follows a von Mises distribution. To improve the consistency of the phase values in the time-frequency domain, we also apply the von Mises distribution to the phase derivatives, i.e., the group delay and the instantaneous frequency. Based on these assumptions, we explore and compare several combinations of loss functions for training our models.
- Categories:
 118 Views
118 Views
- Read more about BREAST CANCER DETECTION BASED ON MERGING FOUR MODES MRI USING CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
The objective of the study is to develop a framework for automatic breast cancer detection with merging four imaging modes. Attempts were made for tumor classification and segmentation; using a multi-parametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) method on breast tumors. MRI data of the breast were obtained from 67 subjects with a 1.5T-MRI scanner. Four imaging modes: were T1 weighted, T2 weighted, Diffusion Weighted and eTHRIVE sequences, and dynamic- contrast-enhanced(DCE)-MRI parameters are acquired.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Modality attention for end-to-end audio-visual speech recognition
- Log in to post comments
Audio-visual speech recognition (AVSR) system is thought to be one of the most promising solutions for robust speech recognition, especially in noisy environment. In this paper, we propose a novel multimodal attention based method for audio-visual speech recognition which could automatically learn the fused representation from both modalities based on their importance. Our method is realized using state-of-the-art sequence-to-sequence (Seq2seq) architectures.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Anomaly Detection in Raw Audio Using Deep Autoregressive Networks
- Log in to post comments
Anomaly detection involves the recognition of patterns outside of what is considered normal, given a certain set of input data. This presents a unique set of challenges for machine learning, particularly if we assume a semi-supervised scenario in which anomalous patterns are unavailable at training time meaning algorithms must rely on non-anomalous data alone. Anomaly detection in time series adds an additional level of complexity given the contextual nature of anomalies.
- Categories:
 312 Views
312 Views
- Read more about Robust Self-Calibration of Constant Offset Time-Difference-of-Arrival
- Log in to post comments
In this paper we study the problem of estimating receiver and sender positions from time-difference-of-arrival measurements, assuming an unknown constant time-difference-of- arrival offset. This problem is relevant for example for repetitive sound events. In this paper it is shown that there are three minimal cases to the problem. One of these (the five receiver, five sender problem) is of particular importance. A fast solver (with run-time under 4 μs) is given.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Speech Emotion Recognition Using Deep Neural Network Considering Verbal and Nonverbal Speech Sounds
- Log in to post comments
Speech emotion recognition is becoming increasingly important for many applications. In real-life communication, non-verbal sounds within an utterance also play an important role for people to recognize emotion. In current studies, only few emotion recognition systems considered nonverbal sounds, such as laughter, cries or other emotion interjection, which naturally exists in our daily conversation. In this work, both verbal and nonverbal sounds within an utterance were thus considered for emotion recognition of real-life conversations.
- Categories:
 148 Views
148 Views