
- Read more about ROBUST AND EFFECTIVE HYPERSPECTRAL PANSHARPENING USING SPATIO-SPECTRAL TOTAL VARIATION
- Log in to post comments
Acquiring high-resolution hyperspectral (HS) images is a very challenging task. To this end, hyperspectral pansharpening techniques have been widely studied, which estimate an HS image of high spatial and spectral resolution (high HS image) from a pair of an HS image of high spectral resolution but low spatial resolution (low HS image) and a high spatial resolution panchromatic (PAN) image.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Optimal Stopping Times for Estimating Bernoulli Parameters with Applications to Active Imaging
- Log in to post comments
We address the problem of estimating the parameter of a Bernoulli process. This arises in many applications, including photon-efficient active imaging where each illumination period is regarded as a single Bernoulli trial. We introduce a framework within which to minimize the mean-squared error (MSE) subject to an upper bound on the mean number of trials. This optimization has several simple and intuitive properties when the Bernoulli parameter has a beta prior.
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views
- Read more about Optimal Spectrum Estimation and System Trade-Off in Long-Distance Frequency-Modulated Continuous-Wave LIDAR
- Log in to post comments
Frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW) LIDAR is a promising technology for next-generation integrated 3D imaging systems. However, it has been considered difficult to apply FMCW LIDAR for long-distance (>100m) targets, such as those in automotive and airborne applications. Maintaining coherence between the reflected beam from the target and locally forwarded beam becomes a significant challenge for tunable laser design.
- Categories:
 59 Views
59 Views
- Read more about CATSEYES: Categorizing Seismic structures with tessellated scattering wavelet networks
- Log in to post comments
As field seismic data sizes are dramatically increasing toward exabytes, automating the labeling of ``structural monads'' --- corresponding to geological patterns and yielding subsurface interpretation --- in a huge amount of available information would drastically reduce interpretation time. Since customary designed features may not account for gradual deformations observable in seismic data, we propose to adapt the wavelet-based scattering network methodology with a tessellation of geophysical images.
- Categories:
 149 Views
149 Views
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views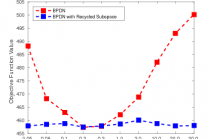
- Read more about ADMM Penalty Parameter Selection with Krylov Subspace Recycling Technique for Sparse Coding
- Log in to post comments
The alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) has been widely used for a very wide variety of imaging inverse problems. One of the disadvantages of this method, however, is the need to select an algorithm parameter, the penalty parameter, that has a significant effect on the rate of convergence of the algorithm. Although a number of heuristic methods have been proposed, as yet there is no general theory providing a good choice of this parameter for all problems.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views- Read more about RGB-D DATA FUSION IN COMPLEX SPACE
- Log in to post comments
Most of the RGB-D fusion methods extract features from RGB
data and depth data separately and then simply concatenate
them or encode these two kinds of features. Such frameworks
cannot explore the correlation between the RGB pixels and
their corresponding depth pixels. Motivated by the physical
concept that range data correspond to the phase change and
color information corresponds to the intensity, we first project
raw RGB-D data into a complex space and then jointly extract
features from the fused RGB-D images. Consequently, the
ICIP_2017.pdf
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views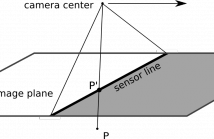
- Read more about Robust Plane-based Calibration for linear cameras
- Log in to post comments
A linear, or 1D, camera is a type of camera that sweeps a linear sensor array over the scene, rather than capturing the scene using a single impression on a 2D sensor array.
They are often used in satellite imagery, industrial inspection, or hyperspectral imaging.
In satellite imaging calibration is often done through a collection of ground points for which the 3D locations are known.
In other applications, e.g. hyperspectral imaging, such known points are not available and annotating many different points is onerous.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about Resolution Enhancement for Hyperspectral Images: A Super-Resolution and Fusion Approach
- Log in to post comments
Many remote sensing applications require a high-resolution hyperspectral image. However, resolutions of most hyperspectral imagers are limited to tens of meters. Existing resolution enhancement techniques either acquire additional multispectral band images or use a pan band image. The former poses hardware challenges, whereas the latter has limited performance. In this paper, we present a new resolution enhancement method that only requires a color image.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views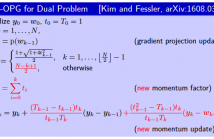
- Read more about Accelerated dual gradient-based methods for total variation image denoising/deblurring problems
- Log in to post comments
icassp-kim.pdf
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views