
- Read more about ECAP-Supplementary
- Log in to post comments
We consider unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) for semantic segmentation in which the model is trained on a labeled source dataset and adapted to an unlabeled target dataset. Unfortunately, current self-training methods are susceptible to misclassified pseudo-labels resulting from erroneous predictions. Since certain classes are typically associated with less reliable predictions in UDA, reducing the impact of such pseudo-labels without skewing the training towards some classes is notoriously difficult.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about When Segment Anything Model Meets Food Instance Segmentation
- Log in to post comments
Here are supplementary materials for the paper "When Segment Anything Model Meets Food Instance Segmentation", which includes an appendix for the paper, examples of FoodInsSeg, examples of InsSAM-Tool, and dataset documentation. These contents aim to provide readers with more details for better understanding the research contributions in this work.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Supplementary Materials: Self-supervised disentangled representation learning of artistic style through Neural Style Transfer
- Log in to post comments
We present a new method for learning a fine-grained representation of visual style. Representation learning aims to discover individual salient features of a domain in a compact and descriptive form that strongly identifies the unique characteristics of that domain. Prior visual style representation works attempt to disentangle style (ie appearance) from content (ie semantics) yet a complete separation has yet to be achieved. We present a technique to learn a representation of visual style more strongly disentangled from the semantic content depicted in an image.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about An Indoor Scene Localization Method Using Graphical Summary of Multi-view RGB-D Images
- Log in to post comments
The graphical summary of multi-view scene can be readily utilized for tasks such as indoor localization. Existing methods for multi-view indoor localization consider the entire scene for localization purposes by assigning equal importance to all components/objects. In this paper, we propose a novel indoor localization method querying a graphical summary of the scene from the graphical summary of the multi-view RGB-D scenes. Salient objects have been utilized to construct the graphical summaries.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about DEEP UNFOLDING NETWORK WITH PHYSICS-BASED PRIORS FOR UNDERWATER IMAGE ENHANCEMENT
- Log in to post comments
We propose an underwater image enhancement algorithm that leverages both model- and learning-based approaches by unfolding an iterative algorithm. We first formulate the underwater image enhancement task as a joint optimization problem, based on the image formation model with physical model and underwater-related priors. Then, we solve the optimization problem iteratively. Finally, we unfold the iterative algorithm so that, at each iteration, the optimization variables and regularizers for image priors are updated by closed-form solutions and learned deep networks, respectively.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about Feature integration via back-projection ordering multi-modal Gaussian process latent variable model for rating prediction
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present a method of feature integration via backprojection ordering multi-modal Gaussian process latent variable model (BPomGP) for rating prediction. In the proposed method, to extract features reflecting the users’ interest, we use the known ratings assigned to the viewed contents and users’ behavior information while viewing the contents which is related to the users’ interest. BPomGP has two important approaches. Unlike the training phase, where the above two types of heterogeneous information are available, behavior information is not given in the test phase.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about SELECTING A DIVERSE SET OF AESTHETICALLY-PLEASING AND REPRESENTATIVE VIDEO THUMBNAILS USING REINFORCEMENT LEARNING
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a new reinforcement-based method for video thumbnail selection (called RL-DiVTS), that relies on estimates of the aesthetic quality, representativeness and visual diversity of a small set of selected frames, made with
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views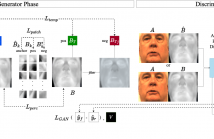
- Read more about WHEN VISIBLE-TO-THERMAL FACIAL GAN BEATS CONDITIONAL DIFFUSION
- Log in to post comments
Thermal facial imagery offers valuable insight into physiological states such as inflammation and stress by detecting emitted radiation in the infrared spectrum, which is unseen in the visible spectra. Telemedicine applications could benefit from thermal imagery, but conventional computers are reliant on RGB cameras and lack thermal sensors. As a result, we propose the Visible-to-Thermal Facial GAN (VTF-GAN) that is specifically designed to generate high-resolution thermal faces by learning both the spatial and frequency domains of facial regions, across spectra.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Early Detection of Cars Exiting Road-side Parking
- Log in to post comments
Vehicles suddenly exiting road-side parking constitute a hazardous situation for vehicle drivers as well as for Connected and Autonomous Vehicles (CAV). In order to improve the awareness of road users, we propose an original cooperative information system based on image processing to monitor vehicles parked on the road-side and on communication for sending early warning to vehicles on the road about vehicles leaving their parking space.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about SEM-CS: SEMANTIC CLIPSTYLER FOR TEXT-BASED IMAGE STYLE TRANSFER
- Log in to post comments
CLIPStyler demonstrated image style transfer with realistic textures using only a style text description (instead of requir- ing a reference style image). However, the ground semantics of objects in the style transfer output is lost due to style spill- over on salient and background objects (content mismatch) or over-stylization. To solve this, we propose Semantic CLIP- Styler (Sem-CS), that performs semantic style transfer.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views