
- Read more about Amplitude Matching: Majorization-Minimization Algorithm For Sound Field Control Only With Amplitude Constraint
- Log in to post comments
ICASSP2021.pdf
- Categories:
 84 Views
84 Views
- Read more about (W)EARABLE MICROPHONE ARRAY AND ULTRASONIC ECHO LOCALIZATION FOR COARSE INDOOR ENVIRONMENT MAPPING
- Log in to post comments
We present a microphone array structure for spherical sound incidence angle tracking that can be attached to headphones or directly integrated into earphones. We show that this microphone array together with an ultrasonic sound source, e.g., a home assistant speaker in the room, allows to estimate the direction and distance of sound reflections on wall surfaces in the room. With our presented method, we achieved sound incidence angle estimation errors of around 14◦
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about Iterative Geometry Calibration from Distance Estimates for Wireless Acoustic Sensor Networks
- Log in to post comments
poster_landscape.pdf
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Iterative Geometry Calibration from Distance Estimates for Wireless Acoustic Sensor Networks
- Log in to post comments
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Translation of a Higher Order Ambisonics Sound Scene Based on Parametric Decomposition
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a novel 3DoF+ system that allows to navigate, i.e., change position, in scene-based spatial audio content beyond the sweet spot of a Higher Order Ambisonics recording. It is one of the first such systems based on sound capturing at a single spatial position. The system uses a parametric decomposition of the recorded sound field. For the synthesis, only coarse distance information about the sources is needed as side information but not the exact number of them.
handout.pdf
- Categories:
 84 Views
84 Views
- Read more about Evaluation of Sensor Self-Noise In Binaural Rendering of Spherical Microphone Array Signals
- Log in to post comments
Spherical microphone arrays are used to capture spatial sound fields, which can then be rendered via headphones. We use the Real-Time Spherical Array Renderer (ReTiSAR) to analyze and auralize the propagation of sensor self-noise through the processing pipeline. An instrumental evaluation confirms a strong global influence of different array and rendering parameters on the spectral balance and the overall level of the rendered noise. The character of the noise is direction independent in the case of spatially uniformly distributed noise.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views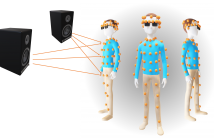
We present an open-access dataset of over 8000 acoustic impulse from 160 microphones spread across the body and affixed to wearable accessories. The data can be used to evaluate audio capture and array processing systems using wearable devices such as hearing aids, headphones, eyeglasses, jewelry, and clothing. We analyze the acoustic transfer functions
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about Learning Dynamic Stream Weights for Linear Dynamical Systems using Natural Evolution Strategies
- Log in to post comments
Multimodal data fusion is an important aspect of many object localization and tracking frameworks that rely on sensory observations from different sources. A prominent example is audiovisual speaker localization, where the incorporation of visual information has shown to benefit overall performance, especially in adverse acoustic conditions. Recently, the notion of dynamic stream weights as an efficient data fusion technique has been introduced into this field.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views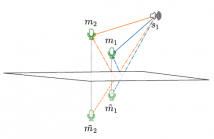
- Read more about MIRAGE: 2D sound source localization using microphone pair augmentation with echoes
- Log in to post comments
It is commonly observed that acoustic echoes hurt perfor-mance of sound source localization (SSL) methods. We in-troduce the concept of microphone array augmentation withechoes (MIRAGE) and show how estimation of early-echocharacteristics can in fact benefit SSL. We propose a learning-based scheme for echo estimation combined with a physics-based scheme for echo aggregation.
- Categories:
 150 Views
150 Views