- Read more about Time-Domain Channel Estimation for Wideband Millimeter Wave Systems With Hybrid Architecture
- Log in to post comments
Millimeter wave (mmWave) systems will likely employ large antennas at both the transmitter and receiver for directional beamforming. Hybrid analog/digital MIMO architectures have been proposed previously for leveraging both array gain and multiplexing gain, while reducing the power consumption in analog-to-digital converters. Channel knowledge is needed to design the hybrid precoders/combiners, which is difficult to obtain due to the large antenna arrays and the frequency selective nature of the channel.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views- Read more about Hybrid Precoding Using Long-term Channel Statistics for Massive MIMO Systems
- Log in to post comments
Hybrid analog/digital precoding in the downlink of multiuser massive MIMO systems can reduce the number of RF chains hence reducing total cost and improving power efficiency. Having few RF chains, however, makes it difficult for a base station to acquire instantaneous channel state information across all antennas. We develop a hybrid technique that uses only long-term (slowly changing) channel statistics in computing the analog precoding matrix. The proposed analog precoder is designed to maximize signal-to-leakage-plusnoise ratio (SLNR) when combined with a baseband precoder.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about Compressed Beam-Selection In Millimeter Wave Systems With Out-of-band Partial Support Information
- Log in to post comments
Compressed beam-selection (CBS) exploits the limited scattering of the millimeter wave (mmWave) channel using compressed sensing (CS) and finds the best beam-pair with limited overhead. The CBS procedure can further benefit from the knowledge of some additional structure in the channel. As mmWave systems are envisioned to be deployed in conjunction with sub-6 GHz systems, we use the spatial information extracted at sub 6 GHz as out-of-band side information about the mmWave channel.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 ViewsWe propose two novel, low-complexity techniques for beam alignment in time division duplexing (TDD) multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems. The techniques are inspired by the power method, an iterative algorithm to determine eigenvalues and eigenvectors through repeated matrix multiplications and improve upon this simple idea by providing a better performance in the low-SNR regime. The first technique sequentially constructs a least-squares estimate of the channel matrix, which is then used to calculate the optimal beamformer/combiner pair.
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about ADC BIT ALLOCATION UNDER A POWER CONSTRAINT FOR MMWAVE MASSIVE MIMO COMMUNICATION RECEIVERS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about Massive MIMO Processing at the Semiconductor Edge: Exploring the System and Circuit Margins for Power Saving
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we consider the potential of processing at the semiconductor edge by allowing voltage over-scaling and complete antenna signal failures, focusing on the per-antenna digital functionality that dominant the DSP complexity. The impact of the resulting hardware errors on the performance of Massive MIMO transmission is analyzed. It shows that the inherent redundancy in the system brings a solid tolerance to sporadic hardware errors. Potential control tactics are introduced, that could further optimize the operation of the error-prone circuitry.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views- Read more about Optimal Transmit Strategy for MIMO Channels with Joint Sum and Per-antenna Power Constraints
- Log in to post comments
This paper studies optimal transmit strategies for multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) Gaussian channels with joint sum and per-antenna power constraints. It is shown that if an unconstraint optimal allocation for an antenna exceeds a per-antenna power constraint, then the maximal power for this antenna is used in the constraint optimal transmit strategy. This observation is then used in an iterative algorithm to compute the optimal transmit strategy in closed-form. Finally, a numerical example is provided to illustrate the theoretical results.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views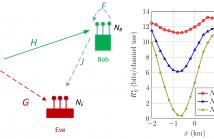
- Read more about A MINORIZATION-MAXIMIZATION (MM) ALGORITHM FOR ARTIFICIAL NOISE (AN)-BASED MIMOME SECRECY RATE MAXIMIZATION
- Log in to post comments
We consider the problem of secrecy rate maximization in a multi-input multi-output multi-eavesdropper (MIMOME) wiretap channel and present an exact solution. A general system model with a multi-antenna eavesdropper and a multi-antenna full-duplex receiver is considered. In particular, we perform joint beamforming and artificial noise optimization in an effort to maximize the achievable secrecy rate. The optimization is performed in the presence of artificial noise generated by both transmitter and legitimate receiver. The resulting optimization problem is non-convex and difficult to solve.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about Achieving High Throughput with Predictive Resource Allocation
- Log in to post comments
Big data analytics makes predicting human behavior possible, but it is unclear how to exploit the predictable information for improving performance of wireless networks. In this paper, we investigate the potential of predictive resource allocation in supporting high throughput by exploiting excess resources. To this end, we assume that the requests and trajectories of mobile users and the average resource usage status of base stations can be predicted within a window.
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views