
- Read more about POWER SPECTRUM OPTIMIZATION FOR CAPACITY OF THE EXTENDED SPECTRUM HYBRID FIBER COAX NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
Capacity requirements of the fixed access network keep increasing towards multi-gigabit connections. For Hybrid Fiber Coaxial (HFC) networks, aggregated rates around 30 Gbit/s can be achieved by increasing the DOCSIS spectrum to 3GHz, assuming a spectral efficiency around 10 bit/s/Hz. Replacement of spectrum limiting components such as passive taps in the HFC network is an efficient way to achieve these data rates, compared with the cost of fiber to the home (FTTH).
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about Computationally Efficient Waveform Design in Spectrally Dense Environment (SAM presentation)
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about Compound Multiple Access Channel with Full-Duplex Amplify-and-Forward Transmitter Cooperations
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about Low-Rank Optimization for Data Shuffling in Wireless Distributed Computing
- Log in to post comments
Wireless distributed computing presents new opportunities to execute intelligent tasks on mobile devices for low-latency applications, by wirelessly aggregating the computation and storage resources among mobile devices. However, for low-latency applications, the key bottleneck lies in the exchange of intermediate results among mobile devices for data shuffling. To improve communication efficiency therein, we establish a novel interference alignment condition by exploiting the locally computed intermediate values as side information.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
- Read more about A compressive sensing-based active user and symbol detection for massive machine type communications
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about Permissible support patterns for identifying the spreading function of time-varying channels
- Log in to post comments
We study support patterns for covariance matrices that appear in the problem of stochastic time-varying channel identification.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about ON ERROR RESILIENT DESIGN OF PREDICTIVE SCALABLE CODING SYSTEMS
- Log in to post comments
Scalable coding is potentially useful in content distribution over unreliable channels, as it enables meaningful reconstruction when the hierarchical bitstream is only partially received. However, its deployment in conjunction with predictive coding may result in considerable performance degradation when errors due to packet loss propagate through the prediction loop. Despite this, most existing predictive scalable coding techniques employ components whose design completely ignores the effects of unreliable channel conditions.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views- Read more about EXPLOITING THE CYCLOSTATIONARITY OF RADAR CHIRP SIGNALS WITH TIME-VARYING FILTERS
- Log in to post comments
A time-varying filter is proposed which improves by 5 dB upon traditional FRESH and Wiener filters when rejecting a pulsed radar signal. The filter is a Time-Varying FRESH (TV-FRESH) filter, which applies different sets of filter weights in a periodic manner, with the same periodicities of the received signal. Matching the periodicities of the filter to that of the signal improves the rejection of interference, producing a better estimate of the desired signal.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views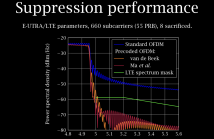
- Read more about Orthogonal Precoding for Sidelobe Suppression in DFT-Based Systems Using Block Reflectors
- Log in to post comments
Sidelobe suppression has always been an important part of crafting communications signals to keep interference with users of adjacent spectrum to a minimum. Systems based on the discrete Fourier transform, such as orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) and single-carrier frequency-division multiple access (SC-FDMA) are especially prone to out-of-band power leakage. Although many techniques have been proposed to suppress sidelobes in DFT-based systems, a satisfactory balance between computational complexity and out-of-band power leakage has remained elusive.
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views