
- Read more about TIME-DOMAIN ACOUSTIC CONTRAST CONTROL WITH A SPATIAL UNIFORMITY CONSTRAINT FOR PERSONAL AUDIO SYSTEMS
- Log in to post comments
Personal audio systems with multiple sound zones for listeners to enjoy different music/audio contents privately in a shared physical space have attracted great research interest in the past two decades. Acoustic Contrast Control (ACC) is one of the most popular methods for generating multiple personal sound zones because it produces the minimum inter-zone interference. However, the ACC method has been found to be inferior to the pressure matching method in terms of sound quality due to an uneven frequency response and nonuniform spatial sound field distribution in the bright zone.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Rotation-Robust Beamforming Based on Sound Field Interpolation with Regularly Circular Microphone Array
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present a novel framework of beamforming robust for a microphone array rotation. In most array signal processing methods, the time-invariant transfer system from a source to a microphone is assumed for calculating a spatial filter. This assumption makes it difficult to use the microphone array in real situations since sources and the microphone array may move. In this work, we focus on one such movement, the array’s rotation. The key in our method is to use a regularly circular microphone array where microphones are equally spaced on a circle’s circumference.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Acoustic analysis and dataset of transitions between coupled rooms
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about ON THE PREDICTABILITY OF HRTFS FROM EAR SHAPES USING DEEP NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
Head-Related Transfer Function (HRTF) individualization is critical for immersive and realistic spatial audio rendering in augmented/virtual reality. Neither measurements nor simulations using 3D scans of head/ear are scalable for practical applications. More efficient machine learning approaches are being explored recently, to predict HRTFs from ear images or anthropometric features. However, it is not yet clear whether such models can provide an alternative for direct measurements or high-fidelity simulations. Here, we aim to address this question.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
- Read more about ICASSP 2021 Poster - SPARSE RECOVERY BEAMFORMING AND UPSCALING IN THE RAY SPACE
- Log in to post comments
We have been exploring the integration of sparse recovery methods into the ray space transform over the past years and now demonstrate the potential and benefits of beamforming and upscaling signals in the integrated ray space and sparse recovery domain. A primary advantage of the ray space approach derives from its robust ability to integrate information from multiple arrays and viewpoints. Nonetheless, for a given viewpoint, the ray space technique requires a dense array that can be divided into sub-arrays enabling the plenacoustic approach to signal processing.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about DIRECTION PRESERVING WIND NOISE REDUCTION OF B-FORMAT SIGNALS - Presentation
- Log in to post comments
Noise reduction in B-format recordings is particularly challenging as it concurrently requires to suppress undesired signals and preserve the spatial properties of the acoustic environment. In particular, wind noise poses an undesirable acoustic condition outdoors. In this work, methods to reduce wind noise while limiting the spatial distortions of the original signal are proposed based on recent works of the present authors.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about DIRECTION PRESERVING WIND NOISE REDUCTION OF B-FORMAT SIGNALS - Poster
- Log in to post comments
Noise reduction in B-format recordings is particularly challenging as it concurrently requires to suppress undesired signals and preserve the spatial properties of the acoustic environment. In particular, wind noise poses an undesirable acoustic condition outdoors. In this work, methods to reduce wind noise while limiting the spatial distortions of the original signal are proposed based on recent works of the present authors.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Translation of a Higher Order Ambisonics Sound Scene Based on Parametric Decomposition
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a novel 3DoF+ system that allows to navigate, i.e., change position, in scene-based spatial audio content beyond the sweet spot of a Higher Order Ambisonics recording. It is one of the first such systems based on sound capturing at a single spatial position. The system uses a parametric decomposition of the recorded sound field. For the synthesis, only coarse distance information about the sources is needed as side information but not the exact number of them.
handout.pdf
- Categories:
 84 Views
84 Views
- Read more about Mutual-Information-Based Sensor Placement for Spatial Sound Field Recording
- Log in to post comments
A sensor (microphone) placement method based on mutual information for spatial sound field recording is proposed. The sound field recording methods using distributed sensors enable the estimation of the sound field inside a target region of arbitrary shape; however, it is a difficult task to find the best placement of sensors. We focus on the mutual-information-based sensor placement method in which spatial phenomena are modeled as a Gaussian process (GP).
- Categories:
 79 Views
79 Views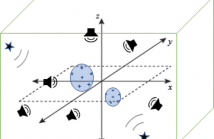
- Read more about Active noise control over multiple regions: performance analysis
- Log in to post comments
Active noise control (ANC) over space is a well-researched topic where multi-microphone, multi-loudspeaker systems are designed to minimize the noise over a spatial region of interest. In this paper, we perform an initial study on the more complex problem of simultaneous noise control over multiple target regions using a single ANC system. In particular, we investigate the maximum active noise control performance over the multiple target regions, given a particular setup of secondary loudspeakers.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views