
- Read more about NON-INTRUSIVE SPEECH QUALITY ASSESSMENT USING NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about DETECTION OF SPOKEN WORDS IN NOISE: COMPARISON OF HUMAN PERFORMANCE TO MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we are interested in assessing the optimality of the human auditory system, when the input stimuli is natural speech that is affected by additive noise. In order to do this, we consider the DANTALE II listening test paradigm of Wagener et al., which has been used to evaluate the intelligibility of noisy speech by exposing human listeners to a selection of constructed noisy sentences. Inspired by this test, we propose a simple model for the communication and classification of noisy speech that takes place in the test.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about DETECTION OF SPOKEN WORDS IN NOISE: COMPARISON OF HUMAN PERFORMANCE TO MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we are interested in assessing the optimality of the human auditory system, when the input stimuli is natural speech that is affected by additive noise. In order to do this, we consider the DANTALE II listening test paradigm of Wagener et al., which has been used to evaluate the intelligibility of noisy speech by exposing human listeners to a selection of constructed noisy sentences. Inspired by this test, we propose a simple model for the communication and classification of noisy speech that takes place in the test.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views
Nasal Finals play an important role in distinguishing lexical meanings in Standard Chinese, but it is still unclear what the primary perceptual cues for nasal Finals are. The present study looks into this question, especially the primary perceptual cues for native Chinese listeners. We conducted two perceptual experiments with three-formant synthetic stimuli in which the second formant (F2) and the third formant (F3) were varied. Experiment I varied F2 and F3 simultaneously in the vowel part (including vowel nucleus and nasalized vowel).
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about EEG Evidence for a Three-Phase Recurrent Process during Spoken Word Processing
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about The Effects of Tone Categories on the Perception of Mandarin Vowels
- Log in to post comments
The boundary positions of /a/-/ɤ/ were significantly different among the four tone conditions, with much less identification of /a/ category under the high-falling tone condition in contrast to the other three tones. Moreover, the maximum identification scores of /ɤ/ category were significantly lower under the falling-rising tone compared with other tone conditions. The relation between F0 and F1, as well as the substantial feature of falling-rising tone might account for these effects of tone categories on Mandarin vowel perception.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about Investigation of the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of the Brain during Perceiving Words
- Log in to post comments
To investigate the temporal dynamics and spatial representations in speech perception and processing, electroencephalograph (EEG) signals were recorded when subjects listening Chinese words and pseudo words.
poster-syk.pdf
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views- Read more about Cognitive Representation of Phonological Categories: The Evidence from Mandarin Speakers’ Learning of Cantonese Tones
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views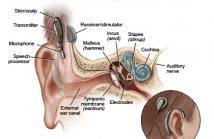
- Read more about The effect of gain thresholds on speech intelligibility for statistical model based noise reduction for cochlear implants:A simulation based verification
- Log in to post comments
Noise corruption can dramatically decrease the speech intelligibility for listeners with cochlear implants (CI). Noise reduction is a key point in CI speech processing strategy. This paper proposes a statistical model based noise reduction algorithm forCIs. A realistic noise estimator, which requires no prior knowledge of the noise, is adopted for noise estimation.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about The Perception of the English Alveolar-velar Nasal Coda Contrast by Monolingual versus Bilingual Chinese Speakers
- Log in to post comments
Relatively little research has addressed the role of L1 in the
perception of English speech contrasts by Chinese learners of
English as L3. The present study investigates the role of L1 in
the perception of the English alveolar-velar nasal coda contrast
(/n/ vs. /ŋ/) after the vowels /i ʌ æ/ by bilingual Changsha
Chinese speakers, whose L1 is Changsha Chinese and L2 is
Standard Mandarin. Changsha Chinese only permits an
alveolar nasal coda /n/, while Standard Mandarin permits both
final /n/ and /ŋ/. We examined whether or not monolingual
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views