
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about ENLLVM: Ensemble based Nonlinear Bayesian Filtering using Linear Latent Variable Models
- Log in to post comments
Real-time nonlinear Bayesian filtering algorithms are overwhelmed by data volume, velocity and increasing complexity of computational models. In this paper, we propose a novel ensemble based nonlinear Bayesian filtering approach which only requires a small number of simulations and can be applied to high-dimensional systems in the presence of intractable likelihood functions.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about Langevin-based Strategy for Efficient Proposal Adaptation in Population Monte Carlo
- Log in to post comments
Population Monte Carlo (PMC) algorithms are a family of
adaptive importance sampling (AIS) methods for approximating
integrals in Bayesian inference. In this paper, we propose
a novel PMC algorithm that combines recent advances
in the AIS and the optimization literatures. In such a way, the
proposal densities are adapted according to the past weighted
samples via a local resampling that preserves the diversity,
but we also exploit the geometry of the targeted distribution.
A scaled Langevin strategy with Newton-based scaling metric
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Active Anomaly Detection with Switching Cost
- Log in to post comments
The problem of anomaly detection among multiple processes is considered within the framework of sequential design of experiments. The objective is an active inference strategy consisting of a selection rule governing which process to probe at each time, a stopping rule on when to terminate the detection, and a decision rule on the final detection outcome. The performance measure is the Bayes risk that takes into account not only sample complexity and detection errors, but also costs associated with switching across processes.
Poster-1.pdf
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Structural Recurrent Neural Network for Traffic Speed Prediction
- Log in to post comments
Deep neural networks have recently demonstrated the traffic prediction capability with the time series data obtained
by sensors mounted on road segments. However, capturing spatio-temporal features of the traffic data often requires a
significant number of parameters to train, increasing computational burden. In this work we demonstrate that embedding
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Structural Recurrent Neural Network for Traffic Speed Prediction
- Log in to post comments
Deep neural networks have recently demonstrated the traffic prediction capability with the time series data obtained by sensors mounted on road segments. However, capturing spatio-temporal features of the traffic data often requires a significant number of parameters to train, increasing computational burden. In this work we demonstrate that embedding topological information of the road network improves the process of learning traffic features.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views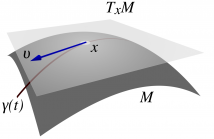
- Read more about Nonlinear State Estimation using Particle Filters on the Stiefel Manifold
- Log in to post comments
Many problems in statistical signal processing involve tracking the state of a dynamic system that evolves on a Stiefel manifold. To this aim, we introduce in this paper a novel particle filter algorithm that approximates the optimal importance function on the Stiefel manifold and is capable of handling nonlinear observation functions. To sample from the required importance function, we develop adaptations of previous MCMC algorithms.
- Categories:
 73 Views
73 Views
- Read more about First-order optimal sequential subspace change-point detection
- Log in to post comments
We consider the sequential change-point detection problem of detecting changes that are characterized by a subspace structure. Such changes are frequent in high-dimensional streaming data altering the form of the corresponding covariance matrix. In this work we present a Subspace-CUSUM procedure and demonstrate its first-order asymptotic optimality properties for the case where the subspace structure is unknown and needs to be simultaneously estimated.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about VECTOR APPROXIMATE MESSAGE PASSING FOR QUANTIZED COMPRESSED SENSING
- Log in to post comments
In recent years approximate message passing algorithms have gained a lot of attention and different versions have been proposed for coping with various system models. This paper focuses on vector approximate message passing (VAMP) for generalized linear models. While this algorithm is originally derived from a message passing point of view, we will review it from an estimation theory perspective and afterwards adapt it for a quantized compressed sensing application. Finally, numerical results are presented to evaluate the performance of the algorithm.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views- Read more about Statistical detection and classification of transient signals in low-bit sampling time-domain signals
- Log in to post comments
We investigate the performance of the generalized Spectral Kurtosis (SK) estimator in detecting and discriminating natural and artificial very short duration transients in the 2-bit sampling time domain Very-Long-Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) data. We demonstrate that, after a 32-bit FFT operation is performed on the 2-bit time domain voltages, these two types of transients become distinguishable from each other in the spectral domain.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views