
- Read more about BNMTRANS: A BRAIN NETWORK SEQUENCE-DRIVEN MANIFOLD-BASED TRANSFORMER FOR COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT DETECTION USING EEG
- Log in to post comments
Early identification of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is crucial for the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease. As neurodegenerative
diseases progress, the synchronous activity observed in electroencephalography (EEG) - which indicates functional connectivity -
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about Unsupervised Relapse Detection using Wearable-Based Digital Phenotyping for The 2nd E-Prevention Challenge
- Log in to post comments
This paper describes SRCB-LUL team's unsupervised relapse detection system submitted to the 2nd E-Prevention Challenge (Psychotic and Non-Psychotic Relapse Detection using Wearable-Based Digital Phenotyping). In our system, a person identification task is added to make the feature extraction network better distinguish between different behavior patterns. Three different structures of the feature extraction network are adopted. Then, the extracted features are used to train an Elliptic Envelope model of each patient for anomaly detection.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views
- Read more about 3D CBCT CHALLENGE 2024: IMPROVED CONE BEAM CT RECONSTRUCTION USING SWINIR-BASED SINOGRAM AND IMAGE ENHANCEMENT
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present our approach to the 3D CBCT Challenge 2024, a part of ICASSP SP Grand Challenges 2024. Improvement in Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) reconstruction has been achieved by integrating Swin Image Restoration (SwinIR) based sinogram and image enhancement modules. The proposed methodology uses Nesterov Accelerated Gradient Descent (NAG) to solve the least squares (NAG-LS) problem in CT image reconstruction.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about Real-Time Privacy-Preserving Fall Risk Assessment with a Single Body-Worn Tracking Camera
- Log in to post comments
Falls are a major cause of injury among elderly adults. In addition, recent research indicates that elderly adults often fall because of the same individual biomechanical causes. Therefore, real-time individual fall risk assessment is crucial for designing a more effective and personalized fall reduction training program. However, existing methods for fall risk assessment either raise privacy concerns or require multiple wearable sensors. In this paper, we propose EgoFall, a real-time privacy-preserving fall risk assessment system using a commercial tracking camera.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views
- Read more about MODEL-BASED LABEL-TO-IMAGE DIFFUSION FOR SEMI-SUPERVISED CHOROIDAL VESSEL SEGMENTATION
- Log in to post comments
Current successful choroidal vessel segmentation methods rely on large amounts of voxel-level annotations on the 3D optical coherence tomography images, which are hard and time-consuming. Semi-supervised learning solves this issue by enabling model learning from both unlabeled data and a limited amount of labeled data. A challenge is the defective pseudo labels generated for the unlabeled data. In this work, we propose a model-based label-to-image diffusion (MLD) framework for semi-supervised choroidal vessel segmentation.
ICASSP_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views- Read more about Semi-Supervised Domain Adaptation for Eeg-Based Sleep Stage Classification
- Log in to post comments
Electroencephalogram (EEG) based sleep stage classification is very important in sleep quality analysis and the treatment of sleep disorders. Deep learning based automated sleep staging has achieved promising performance. However, it has not been widely adopted in clinical practice, due to the domain shift problem and insufficient labeled training data, especially for patients. To cope with these problems, this paper proposes a Transformer-based semi-supervised domain adaptation (SSDA) approach for EEG-based sleep stage classification.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about EEG-BASED FAST AUDITORY ATTENTION DETECTION IN REAL-LIFE SCENARIOS USING TIME-FREQUENCY ATTENTION MECHANISM
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Auditory attention detection (AAD) based on electroencephalogram (EEG) helps recognize the target speaker in a cocktail party scenario, advancing auditory brain-computer interface development. Previous EEG studies on AAD were largely based on data collected in laboratory settings. In this study, we investigated the AAD with EEG data collected when subjects were walking and sitting in real-life scenarios. To improve the detection accuracy, we proposed the time-frequency attention mechanism to the convolution neural network on EEG data.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Poster for "Graph-based permutation patterns for the analysis of task-related fMRI signals on DTI networks in mild cognitive impairment"
- Log in to post comments
Permutation Entropy (PE) is a powerful nonlinear analysis technique for univariate time series. Recently, Permutation Entropy for Graph signals (PE_G) has been proposed to extend PE to data residing on irregular domains. However, PE_G is limited as it provides a single value to characterise a whole graph signal. Here, we introduce a novel approach to evaluate graph signals at the vertex level: graph-based permutation patterns. Synthetic datasets show the efficacy of our method.
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views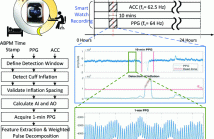
- Read more about MAML-Based 24-Hour Personalized Blood Pressure Estimation from Wrist Photoplethysmography Signals in Free-Living Context
- Log in to post comments
Systolic blood pressure (BP) variability at daytime and nighttime, also known as BP dip, has shown its clinical value in diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). A model agnostic meta learning (MAML)-based 24-hour personalized approach is proposed in this paper for BP estimation using wrist photoplethysmography (PPG) signals from smart watch in free-living context.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views
- Read more about TRLS: A TIME SERIES REPRESENTATION LEARNING FRAMEWORK VIA SPECTROGRAM FOR MEDICAL SIGNAL PROCESSING
- Log in to post comments
Representation learning frameworks in unlabeled time series have been proposed for medical signal processing. Despite the numerous excellent progresses have been made in previous works, we observe the representation extracted for the time series still does not generalize well. In this paper, we present a Time series (medical signal) Representation Learning framework via Spectrogram (TRLS) to get more informative representations. We transform the input time-
- Categories:
 81 Views
81 Views