
- Read more about Distributed Scheduling Algorithms for Optimizing Information Freshness in Wireless Networks
- Log in to post comments
Age of Information (AoI), measures the time elapsed since the last received information packet was generated at the source. We consider the problem of AoI minimization for single-hop flows in a wireless network, under pairwise interference constraints and time varying channel. We consider simple, yet broad, class of distributed scheduling policies, in which a transmission is attempted over each link with a certain attempt probability. We obtain an interesting relation between the optimal attempt probability and the optimal AoI of the link, and its neighboring links.
- Categories:
 64 Views
64 Views
- Read more about Self-Adaptive Energy Efficient Operation in UAV-assisted Public Safety Networks
- Log in to post comments
Public Safety Networks (PSN) are expected to provide resilient communication paradigms under disaster recovery scenarios. Towards providing an energy efficient solution an UAV-supported multi-level architecture is employed where user equipments (UEs) are grouped together in clusters.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Coordinated Hybrid Precoding for Energy-efficient Millimeter Wave Systems
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views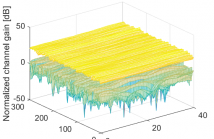
- Read more about Channel Hardening in Massive MIMO - a Measurement Based Analysis
- Log in to post comments
Wireless-controlled robots, cars and other critical applications are in need of technologies that offer high reliability and low latency. Massive MIMO, Multiple-Input Multiple-Output, is a key technology for the upcoming 5G systems and is one part of the solution to increase the reliability of wireless systems. More specifically, when increasing the number of base station antennas in a massive MIMO systems the channel variations decrease and the so-called channel hardening effect appears. This means that the variations of the channel gain in
chhard_mamimo_spawc.pdf
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about LQG Control and Scheduling Co-design for Wireless Sensor and Actuator Networks
- Log in to post comments
We study a co-design problem of control, scheduling, and routing over a multi-hop sensor and actuator network (WSANs) subject to energy-saving consideration. We formulate an optimization problem, minimizing a linear combination of the averaged linear quadratic Gaussian (LQG) control performance and the averaged transmission energy consumption. Optimal solutions are derived and their performance is illustrated in a numerical example.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Mobile Edge Computing for Cellular-Connected UAV: Computation Offloading and Trajectory Optimization
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views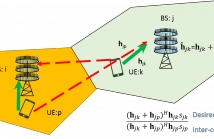
- Read more about Pilot Contamination in Massive MIMO: A Measurement-based Analysis using 2D-MUSIC
- Log in to post comments
When a base station (BS) sees desired and interfering
users at different angles, it results in non-overlapping angleof-
arrival (AoA) regions for those users. This is important for
reducing pilot contamination (PC) of massive MIMO systems.
Most state of the art studies utilize a simple non-line-of-sight
(NLoS) one-ring model which assumes sparse support and can
reasonably schedule users with different AoA to minimize PC.
However, it is not confirmed with measurements that the one-ring
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Random Access Schemes in Wireless Systems With Correlated User Activity
- Log in to post comments
Traditional random access schemes are designed based on the aggregate process of user activation, which is created on the basis of independent activations of the users. However, in Machine-Type Communications (MTC), some users are likely to exhibit a high degree of correlation, e.g. because they observe the same physical phenomenon. This paves the way to devise access schemes that combine scheduling and random access, which is the topic of this work. The underlying idea is to schedule highly correlated users in such a way that their transmissions are less likely to result in a collision.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Resource Allocation for Solar Powered UAV Communication Systems
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we investigate the resource allocation design for multicarrier (MC) systems employing a solar powered unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) for providing communication services to multiple downlink users. We study the joint design of the three-dimensional positioning of the UAV and the power and subcarrier allocation for maximization of the system sum throughput. The algorithm design is formulated as a mixed-integer non-convex optimization problem, which requires a prohibitive computational complexity for obtaining the globally optimal solution.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about High-speed Optical Camera Communication Using an Optimally Modulated Signal
- Log in to post comments
This paper describes a high-speed optical camera communication (OCC) technique using an LED and a rolling-shutter camera. In the proposed technique, the symbols being transmitted are encoded as time delays of optimally modulated signals derived theoretically. A receiver decodes the symbols by using intensities obtained from four consecutive line sensors of a camera.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views