
- Read more about Tag Antenna Structure Calibrated Backscattering Signal Detection
- Log in to post comments
Backscatter Communication (BackCom) is gaining popularity due to its potential for sustainable and low-cost Internet of Things (IoT) applications. However, due to the limited resources of passive tags, optimizing the backscatter modulation is critical for the widespread use of this technology. Current backscatter modulation designs ignore the impact of the tag’s antenna structure, which we show in this paper to have a negative effect on system performance and
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views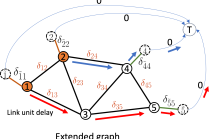
- Read more about Congestion-aware Distributed Task Offloading in Wireless Multi-hop Networks using Graph Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
Computational offloading has become an enabling component for edge intelligence in mobile and smart devices. Existing offloading schemes mainly focus on mobile devices and servers, while ignoring the potential network congestion caused by tasks from multiple mobile devices, especially in wireless multi-hop networks. To fill this gap, we propose a low-overhead, congestion-aware distributed task offloading scheme by augmenting a distributed greedy framework with graph-based machine learning.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views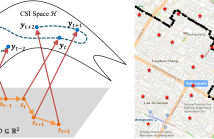
- Read more about HMM-Based CSI Embedding for Trajectory Recovery from RSS Measurements of Non-Cooperative Devices
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Constructing \ac{csi} maps may help wireless communications and localization. However, CSI map construction requires up-to-date CSI measurement data with location labels, which induces a huge challenge in practice. Conventional CSI embedding methods project the CSI to a low dimensional latent space which may not have a clear physical meaning for localization purpose. This paper attempts to extract the user locations from CSI measurements and recover the trajectory of the user in an outdoor vehicular communication scenario.
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views
The three-dimensional (3D) location optimization for reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) aided millimeter wave network is investigated. We first formulate the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) maximization model by jointly optimizing the precoding vector, the RIS location and its parameter matrix in a multiple-input single-output downlink network. The optimal maximum ratio transmission precoding is applied, and the alternating direction method of multipliers is proposed for the highly nonlinear combinatorial problem.
ICASSP.pdf
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
The on-going paradigm shift knocking on the door of future wireless communication system is ubiquitous Internet of Things (IoT), and the maturity of which will be hindered by the challenges related to security. Artificial intelligence (AI) is proficient in solving intractable optimization problems in a data-based way, which provides a new idea for network security and physical-layer guarantee. In this paper, we divide the ubiquitous IoT networks into cyberspace and electromagnetic space, and identify the threat models.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Read more about QuantPipe: Applying Adaptive Post-Training Quantization for Distributed Transformer Pipelines in Dynamic Edge Environments
- Log in to post comments
Pipeline parallelism has achieved great success in deploying large-scale transformer models in cloud environments, but has received less attention in edge environments. Unlike in cloud scenarios with high-speed and stable network interconnects, dynamic bandwidth in edge systems can degrade distributed pipeline performance. We address this issue withQuantPipe, a communication-efficient distributed edge system that introduces post-training quantization (PTQ) to compress the communicated tensors.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Lossy Compression of Gaussian Source Using Low Density Generator Matrix Codes
- Log in to post comments
We present a tandem scheme for Gaussian source compression, where a dead-zone quantizer is concatenated with a ternary low density generator matrix (LDGM) code. Both theoretical analysis and simulation results show that the LDGM codes can be universally optimal for near-lossless compression of ternary sources. Consequently, the distortion with the tandem scheme is mainly caused by the quantization, which can be negligible for high-rate quantizer. The most distinguished feature of the proposed scheme is its flexibility.
- Categories:
 64 Views
64 Views

In the paper Huffman codes that mix different r-nary code elements in one code, the mixed Huffman codes, are analyzed. The Huffman code generalization usually leads to shortening of average codeword length: a statistical test shows that for source alphabets longer than 8-12 elements more than 99% of the best compact codes are mixed Huffman ones. This is also true for practical mixed Huffman codes, which is demonstrated in experiments with data files containing up to milion elements for sources of size 12-17 symbols.
- Categories:
 145 Views
145 Views
- Read more about FEDERATED TRACE: A NODE SELECTION METHOD FOR MORE EFFICIENT FEDERATED LEARNING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views