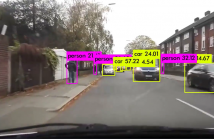
This paper proposed a modified YOLOv3 which has an extra object depth prediction module for obstacle detection and avoidance. We use a pre-processed KITTI dataset to train the proposed, unified model for (i) object detection and (ii) depth prediction and use the AirSim flight simulator to generate synthetic aerial images to verify that our model can be applied in different data domains.
- Categories:
 291 Views
291 Views
- Read more about Accurate 3D Cell Segmentation Using Deep Features and CRF Refinement
- Log in to post comments
ICIP2019_2.pdf
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Expression Conditional GAN for Facial Expression-To-Expression Translation
- 2 comments
- Log in to post comments
ICIP19_3236.pptx
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views
- Read more about High-Accuracy Automatic Person Segmentation with Novel Spatial Saliency Map
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we propose a person segmentation system that achieves high segmentation accuracy with a much smaller CNN network. In this approach, key-point detection annotation is incorporated for the first time and a novel spatial saliency map, in which the intensity of each pixel indicates the likelihood of forming a part of the human and reflects the distance from the body, is generated to provide more spatial information.
- Categories:
 75 Views
75 Views
- Read more about A Collaborative Algorithmic Framework to Track Objects And Events
- Log in to post comments
One faces several challenges when tracking objects and events simultaneously in multi-camera environments — especially if the events associated with the object require precise knowledge of the pose of the object at each instant of time. To illustrate the challenges involved, we consider the problem of tracking bins and their contents at airport security checkpoints. The pose of each bin must be tracked with precision in order to minimize the errors associated with the detection of the various items that the passengers may place in the bins and/or take out of them.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Adaptive Fusion-based 3D Keypoint Detection for RGB Point Clouds
- Log in to post comments
We propose a novel keypoint detector for 3D RGB Point Clouds (PCs). The proposed keypoint detector exploits both the 3D structure and the RGB information of the PC data. Keypoint candidates are generated by computing the eigenvalues of the covariance matrix of the PC structure information. Additionally, from the RGB information, we estimate the salient points by an efficient adaptive difference of Gaussian-based operator. Finally, we fuse the resulting two sets of salient points to improve the repeatability of the 3D keypoint detector.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about PHOTO STYLE TRANSFER WITH CONSISTENCY LOSSES
- Log in to post comments
We address the problem of style transfer between two photos and propose a new way to preserve photorealism. Using the single pair of photos available as input, we train a pair of deep convolution networks (convnets), each of which transfers the style of one photo to the other. To enforce photorealism, we introduce a content preserving mechanism by combining a cycle-consistency loss with a self-consistency loss. Experimental results show that this method does not suffer from typical artifacts observed in methods working in the same settings.
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views
- Read more about Toward Visual Voice Activity Detection for Unconstrained Videos
- Log in to post comments
The prevalent audio-based Voice Activity Detection (VAD) systems are challenged by the presence of ambient noise and are sensitive to variations in the type of the noise. The use of information from the visual modality, when available, can help overcome some of the problems of audio-based VAD. Existing visual-VAD systems however do not operate directly on the whole image but require intermediate face detection, face landmark detection and subsequent facial feature extraction from the lip region.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about LANGUAGE AND VISUAL RELATIONS ENCODING FOR VISUAL QUESTION ANSWERING
- Log in to post comments
Visual Question Answering (VQA) involves complex relations of two modalities, including the relations between words and between image regions. Thus, encoding these relations is important to accurate VQA. In this paper, we propose two modules to encode the two types of relations respectively. The language relation encoding module is proposed to encode multi-scale relations between words via a novel masked selfattention. The visual relation encoding module is proposed to encode the relations between image regions.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Image Super-Resolution using CNN Optimised by Self-Feature Loss
- Log in to post comments
Despite the success of state-of-the-art single image superresolution algorithms using deep convolutional neural networks in terms of both reconstruction accuracy and speed of execution, most proposed models rely on minimizing the mean square reconstruction error. More recently, inspired by transfer learning, Mean Square Error (MSE)-based content loss estimation has been replaced with loss calculated on feature maps of the pre-trained networks, e.g. VGG-net used for ImageNet classification.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views