
- Read more about LIP IMAGE SEGMENTATION IN MOBILE DEVICES BASED ON ALTERNATIVE KNOWLEDGE DISTILLATION
- Log in to post comments
Lip image segmentation, as the first step in many lip-related tasks (e.g. automatic lipreading), is of vital significance for the subsequent procedures. Nowadays, with the increasing computational power of the mobile devices, mobile applications become more and more popular. In this paper, a new approach is proposed, which is able to segment the lip region in natural scenes and is of acceptable computational complexity to be implemented in mobile devices. Two networks including a complex teacher network and a compact student network with the same structure are employed.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about VIEWPOINT ESTIMATION IN IMAGES BY A KEY-POINT BASED DEEP NEURAL NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
Viewpoint estimation in a 2D image is a challenging task due to the great variations in the object’s shape, appearance,
visible parts, etc. To overcome the above difficulties, a new deep neural network is proposed, which employs the key-points of the object as a regularization term and a semantic bridge connecting the raw pixels with the object’s viewpoint. A series of Hourglass structures are adopted for key-point
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views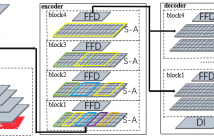
- Read more about TEXT RECOGNITION IN IMAGES BASED ON TRANSFORMER WITH HIERARCHICAL ATTENTION
- Log in to post comments
Recognizing text in images has been a hot research topic in computer vision for decades due to its various application. However, the variations in text appearance in term of perspective distortion, text line curvature, text styles, etc., cause great trouble in text recognition. Inspired by the Transformer structure that achieved outstanding performance in many natural language processing related applications, we propose a new Transformer-like structure for text recognition in images, which is referred to as the Hierarchical Attention Transformer Network (HATN).
- Categories:
 100 Views
100 Views
- Read more about Context-Aware Automatic Occlusion Removal
- Log in to post comments
Occlusion removal is an interesting application of image enhancement, for which, existing work suggests manually-
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about Violence Rating Prediction with Rank Learning
- Log in to post comments
Children's exposure to violence has become a severe problem with the rapid development of Internet. Recognizing violent video and estimating violence extent become crucial. Most researches focus on violent scene or violent action detection, lacking overall violence extent information. In this paper, we propose a violence rating prediction approach and build a novel violent video dataset.
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views- Read more about Simulation Framework for a Visual-Inertial Navigation System
- Log in to post comments
The ability to test methods based on simulated data is an important component in the development of intelligent localization systems at the present time. This includes the replication of realistic environments and sensors on the one hand. On the other hand, an implementation of a correct movement profile of the target mobile platform is required. This is complicated by the large variety of possible platform variants. We propose a method to transfer movement profiles that have been recorded in real world into a simulation environment.
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views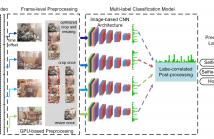
- Read more about A REAL-TIME MULTI-LABEL CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM FOR SHORT VIDEOS
- Log in to post comments
Efficient classification of short videos is of a great challenge in industry due to their large amounts and diverse semantics. In this paper, we present a real-time multi-label classification system to attain it. Specifically, a frame-level preprocessing strategy is first proposed to efficiently decode the videos for useful information. Then an image-based model is developed to achieve the final video-level classification.
- Categories:
 167 Views
167 Views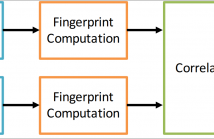
- Read more about Detection and Synchronization of Video Sequences for Event Reconstruction
- Log in to post comments
With an ever-growing amount of unexpected menaces in crowded places such as terrorist attacks, it is paramount to develop techniques to aid investigators reconstructing all details about an event of interest. To extract reliable information about the event, all kinds of available clues must be jointly exploited. As a matter of fact, today's sources of information are plenty and varied, as important events affecting many people are typically documented by different sources.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about Deep Face Verification for Spherical Images
- Log in to post comments
Over the years, several problems regarding the analysis of face images have been addressed, including face detection, recognition, identification, and verification. The advent of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) gave rise to a drastic improvement on state-of-the-art performances for these problems.
ICIP 360.pdf
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views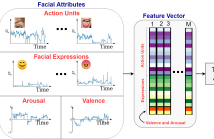
- Read more about A Facial Affect Analysis System for Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we introduce an end-to-end machine learning-based system for classifying autism spectrum disorder (ASD) using facial attributes such as expressions, action units, arousal, and valence. Our system classifies ASD using representations of different facial attributes from convolutional neural networks, which are trained on images in the wild. Our experimental results show that different facial attributes used in our system are statistically significant and improve sensitivity, specificity, and F1 score of ASD classification by a large margin.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views