
- Read more about AASIST: AUDIO ANTI-SPOOFING USING INTEGRATED SPECTRO-TEMPORAL GRAPH ATTENTION NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 90 Views
90 Views
- Read more about MULTI-QUERY MULTI-HEAD ATTENTION POOLING AND INTER-TOPK PENALTY FOR SPEAKER VERIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
This paper describes the multi-query multi-head attention (MQMHA)
pooling and inter-topK penalty methods which were first proposed in
our submitted system description for VoxCeleb speaker recognition
challenge (VoxSRC) 2021. Most multi-head attention pooling mechanisms either attend to the whole feature through multiple heads or
attend to several split parts of the whole feature. Our proposed
MQMHA combines both these two mechanisms and gain more
diversified information. The margin-based softmax loss functions
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views
- Read more about RawNeXt: Speaker verification system for variable-duration utterances with deep layer aggregation and extended dynamic scaling policies
- Log in to post comments
Despite achieving satisfactory performance in speaker verification using deep neural networks, variable-duration utterances remain a challenge that threatens the robustness of systems. To deal with this issue, we propose a speaker verification system called RawNeXt that can handle input raw waveforms of arbitrary length by employing the following two components: (1) A deep layer aggregation strategy enhances speaker information by iteratively and hierarchically aggregating features of various time scales and spectral channels output from blocks.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about GRAPH ATTENTIVE FEATURE AGGREGATION FOR TEXT-INDEPENDENT SPEAKER VERIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
The objective of this paper is to combine multiple frame-level features into a single utterance-level representation considering pair wise relationships. For this purpose, we propose a novel graph attentive feature aggregation module by interpreting each frame-level feature as a node of a graph. The inter-relationship between all possible pairs of features, typically exploited indirectly, can be directly modeled using a graph. The module comprises a graph attention layer and a graph pooling layer followed by a readout operation.
- Categories:
 65 Views
65 Views
- Read more about Graph Convolutional Network Based Semi-Supervised Learning on Multi-Speaker Meeting Data
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about A study of the robustness of raw waveform based speaker embeddings under mismatched conditions
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we conduct a cross-dataset study on parametric and non-parametric raw-waveform based speaker embeddings through speaker verification experiments. In general, we observe a more significant performance degradation of these raw-waveform systems compared to spectral based systems. We then propose two strategies to improve the performance of raw-waveform based systems on cross-dataset tests. The first strategy is to change the real-valued filters into analytic filters to ensure shift-invariance.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views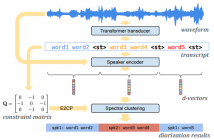
- Read more about Turn-to-Diarize: Online Speaker Diarization Constrained by Transformer Transducer Speaker Turn Detection
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present a novel speaker diarization system for streaming on-device applications. In this system, we use a transformer transducer to detect the speaker turns, represent each speaker turn by a speaker embedding, then cluster these embeddings with constraints from the detected speaker turns. Compared with conventional clustering-based diarization systems, our system largely reduces the computational cost of clustering due to the sparsity of speaker turns.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about Robust self-supervised speaker representation learning via instance mix regularization
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 58 Views
58 Views
- Read more about Multi-View Self-Attention based Transformer for Speaker Recognition
- Log in to post comments
Initially developed for natural language processing (NLP), Transformer model is now widely used for speech processing tasks such as speaker recognition, due to its powerful sequence modeling capabilities. However, conventional self-attention mechanisms are originally designed for modeling textual sequence without considering the characteristics of speech and speaker modeling. Besides, different Transformer variants for speaker recognition have not been well studied.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about DISENTANGLED SPEAKER EMBEDDING FOR ROBUST SPEAKER VERIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
Entanglement of speaker features and redundant features may lead to poor performance when evaluating speaker verification systems on an unseen domain. To address this issue, we propose an InfoMax domain separation and adaptation network (InfoMax–DSAN) to disentangle the domain-specific features and domain-invariant speaker features based on domain adaptation techniques. A frame-based mutual information neural estimator is proposed to maximize the mutual information between frame-level features and input acoustic features, which can help retain more useful information.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views