- Read more about I-VECTOR/PLDA SPEAKER RECOGNITION USING SUPPORT VECTORS WITH DISCRIMINANT ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
i-Vector feature representation with probabilistic linear discriminant analysis (PLDA) scoring in speaker recognition system has recently achieved effective performance even on channel mismatch conditions. In general, experiments carried out using this combined strategy employ linear discriminant analysis (LDA) after the i-Vector extraction phase to suppress irrelevant directions, such as those introduced by noise or channel distortions. However, speaker-related and -non-related variability present in the data may prevent LDA from finding the best projection matrix.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views- Read more about APPLYING COMPENSATION TECHNIQUES ON I-VECTORS EXTRACTED FROM SHORT-TEST UTTERANCES FOR SPEAKER VERIFICATION USING DEEP NEURAL NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
We propose a method to improve speaker verification performance when a test utterance is very short. In some situations with short test utterances, performance of i-vector/probabilistic linear discriminant analysis systems degrades. The proposed method transforms short-utterance feature vectors to adequate vectors using a deep neural network, which compensate for short utterances.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views- Read more about SPEAKER SEGMENTATION USING DEEP SPEAKER VECTORS FOR FAST SPEAKER CHANGE SCENARIOS
- Log in to post comments
A novel speaker segmentation approach based on deep neural network is proposed and investigated. This approach uses deep speaker vectors (d-vectors) to represent speaker characteristics and to find speaker change points. The d-vector is a kind of frame-level speaker recognition feature, whose discriminative training process corresponds to the goal of discriminating a speaker change point from a single speaker speech segment in a short time window.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about EXPLORING UNIVERSAL SPEECH ATTRIBUTES FOR SPEAKER VERIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
The universal speech attributes for speaker verification (SV)
are addressed in this paper. The aim of this work is to
exploit fundamental characteristics across different speakers
within the deep neural network (DNN)/i-vector framework.
The manner and place of articulation form the fundamental
speech attribute unit inventory, and new attribute units for
acoustic modelling are generated by a two-step automatic
clustering method in this paper. The DNN based on
universal attribute units is used to generate posterior
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about Senone I-Vectors for Robust Speaker Verification
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views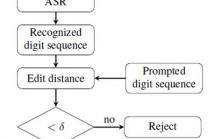
- Read more about Digit-dependent Local I-Vector for Text-Prompted Speaker Verification with Random Digit Sequences
- Log in to post comments
The widely adopted i-vector performances well in text-independent speaker verification with long speech duration. How to integrate the state-of-the-art i-vector framework into the text-prompted speaker verification is addressed in this paper. To take advantage of the lexical information and enhance the performance for speaker verification with random digit sequences, this paper proposes to extract a set of digit-dependent local i-vectors from the utterance instead of extracting a single i-vector. The digit-dependent local i-vector is considered
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views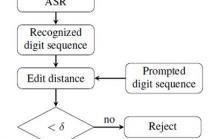
- Read more about Digit-dependent Local I-Vector for Text-Prompted Speaker Verification with
- Log in to post comments
The widely adopted i-vector performances well in textindependent speaker verification with long speech duration.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views- Read more about A study of variational method for text-independent speaker recognition
- Log in to post comments
An i-vector has become the state-of-the-art algorithm for text-independent recognition. Most of related works take the extraction of the i-vector as a black-box by using some open software (e.g. Kaldi, Alize) and focus on the vector-based back-end algorithms, such as length normalization, WCCN, or PLDA. In this paper, we study the variational method and present a concise derivation for the i-vector. Based on our proposed methods, three criteria for derivation are compared. There are maximum likelihood (ML), maximum a posteriori (MAP) and maximum
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views- Read more about First Investigation of Universal Speech Attributes for Speaker Verification
- Log in to post comments
The universal speech attributes to speaker verification (SV) is addressed in this paper. The manner and place of articulation form the universal attribute unit inventory, and deep neural network (DNN) is used as acoustic model.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views