
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

We introduce a sequential Bayesian binary hypothesis testing problem under social learning, termed selfish learning, where agents work to maximize their individual rewards. In particular, each agent receives a private signal and is aware of decisions made by earlier-acting agents. Beside inferring the underlying hypothesis, agents also decide whether to stop and declare, or pass the inference to the next agent. The employer rewards only correct responses and the reward per worker decreases with the number of employees used for decision making.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about Recovery of noisy points on band-limited surfaces
- Log in to post comments
We introduce a continuous domain framework for the recovery of points on a surface in high dimensional space, represented as the zero-level set of a bandlimited function. We show that the exponential maps of the points on the surface satisfy annihilation relations, implying that they lie in a finite dimensional subspace. The subspace properties are used to derive sampling conditions, which will guarantee the perfect recovery of the surface from finite number of points.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views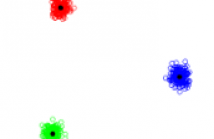
- Read more about Clustering of data with missing entries
- Log in to post comments
The analysis of large datasets is often complicated by the presence of missing entries, mainly because most of the current machine learning algorithms are designed to work with full data. The main focus of this work is to introduce a clustering
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
In this paper, we propose an extension of guided image filtering to support arbitrary window functions. The guided image filtering is a fast edge-preserving filter based on a local linearity assumption. The filter supports not only image smoothing but also edge enhancement and image interpolation. The guided image filter assumes that an input image is a local linear transformation of a guidance image, and the assumption is supported in a local finite region. For realizing the supposition, the guided image filtering consists of a stack of box filtering.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views- Read more about Short packet structure for ultra-reliable machine-type communication: tradeoff between detection and decoding
- Log in to post comments
Machine-type communication requires rethinking of the structure of short packets due to the coding limitations and the significant role of the control information. In ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), it is crucial to optimally use the limited degrees of freedom (DoFs) to send data and control information. We consider a URLLC model for short packet transmission with acknowledgement (ACK).
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about Joint source localization and dereverberation by sound field interpolation using sparse regularizations (slides)
- Log in to post comments
n this paper, source localization and dereverberation are formulated jointly as an inverse problem. The inverse problem consists in the interpolation of the sound field measured by a set of microphones by matching the recorded sound pressure with that of a particular acoustic model. This model is based on a collection of equivalent sources creating either spherical or plane waves. In order to achieve meaningful results, spatial, spatio-temporal and spatio-spectral sparsity can be promoted in the signals originating from the equivalent sources.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Crowdsourced Pairwise-Comparison for Source Separation Evaluation
- Log in to post comments
Automated objective methods of audio source separation evaluation are fast, cheap, and require little effort by the investigator. However, their output often correlates poorly with human quality assessments and typically require ground-truth (perfectly separated) signals to evaluate algorithm performance. Subjective multi-stimulus human ratings (e.g. MUSHRA) of audio quality are the gold standard for many tasks, but they are slow and require a great deal of effort to recruit participants and run listening tests.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Investigating the Effect of Sound-Event Loudness on Crowdsourced Audio Annotations
- Log in to post comments
Audio annotation is an important step in developing machine-listening systems. It is also a time consuming process, which has motivated investigators to crowdsource audio annotations. However, there are many factors that affect annotations, many of which have not been adequately investigated. In previous work, we investigated the effects of visualization aids and sound scene complexity on the quality of crowdsourced sound-event annotations.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about GM-PHD Filter Based Online Multiple Human Tracking using Deep Discriminative Correlation Matching
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views
- Read more about Generative ScatterNet Hybrid Deep Learning (G-SHDL) Network with Structural priors for Semantic Image Segmentation
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views