
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Limiting Numerical Precision of Neural Networks to Achieve Real-time Voice Activity Detection
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about TIC-TAC, FORGERY TIME HAS RUN-UP! LIVE ACOUSTIC WATERMARKING FOR INTEGRITY CHECK IN FORENSIC APPLICATIONS
- Log in to post comments
A common problem in audio forensics is the difficulty to
authenticate an audio recording. In this paper we provide a novel
and reliable solution to this problem by making use of a control
signal, visible and audible on the actual recording, yet ignored by
the listener, the TIC-TAC signal. We describe our live watermark
solution, we incorporate it in an integrity check algorithm and we
provide meaningful preliminary tests. Their results, computed in
terms of precision show an outstanding performance: 100%
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views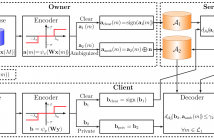
- Read more about Privacy-Preserving Outsourced Media Search Using Secure Sparse Ternary Codes
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a privacy-preserving framework for outsourced media search applications. Considering three parties, a data owner, clients and a server, the data owner outsources the description of his data to an external server, which provides a search service to clients on the behalf of the data owner. The proposed framework is based on a sparsifying transform with ambiguization, which consists of a trained linear map, an element-wise nonlinearity and a privacy amplification.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about DIRECT, NEAR REAL TIME ANIMATION OF A 3D TONGUE MODEL USING NON-INVASIVE ULTRASOUND IMAGES
- Log in to post comments
A new technique for representing speech articulation with
an ultrasound-driven finite element model of the tongue is
presented. By using a snake contour extraction algorithm
with anatomically motivated constraints and a common
coordinate system between the ultrasound and the tongue
model, it is possible for the first time to obtain a realistic 3D
simulation of the tongue directly from a non-invasive sensor
(ultrasound), without mapping through any intermediate
sensor modalities, and at near real-time frame rates.
ICASSP.pptx
ICASSP.pptx
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about MODEL BASED DEEP LEARNING IN FREE BREATHING, UNGATED, CARDIAC MRI RECOVERY
- Log in to post comments
We introduce a model-based reconstruction
framework with deep learned (DL) and smoothness regularization
on manifolds (STORM) priors to recover free
breathing and ungated (FBU) cardiac MRI from highly undersampled
measurements. The DL priors enable us to exploit
the local correlations, while the STORM prior enables
us to make use of the extensive non-local similarities that are
subject dependent. We introduce a novel model-based formulation
that allows the seamless integration of deep learning
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about INVESTIGATION IN SPATIAL-TEMPORAL DOMAIN FOR FACE SPOOF DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
This paper focuses on face spoofing detection using video. The purpose is to find out the best scheme for this task in the end-to-end learning manner. We investigate 4 different types of structure to fully exploit the raw data in its spatial-temporal domain, which are the pure CNN, CNN with 3D convolu-tion, CNN+LSTM and CNN+Conv-LSTM. Moreover, anoth-er stream built on optical flow is also used, and with a proper fusion method, it can improve the accuracy. In experiments, we compare schemes on the raw data in single stream and fusion methods with optical flow in two streams.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about AN UPPER BOUND ON THE REQUIRED SIZE OF A NEURAL NETWORK CLASSIFIER
- Log in to post comments
There is growing interest in understanding the impact of architectural parameters such as depth, width, and the type of
activation function on the performance of a neural network. We provide an upper-bound on the number of free parameters
a ReLU-type neural network needs to exactly fit the training data. Whether a net of this size generalizes to test data will
be governed by the fidelity of the training data and the applicability of the principle of Occam’s Razor. We introduce the
- Categories:
 144 Views
144 Views
- Read more about TENSOR-BASED NONLINEAR CLASSIFIER FOR HIGH-ORDER DATA ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about DESIGN OF OPTIMAL ENTROPY-CONSTRAINED UNRESTRICTED POLAR QUANTIZER FOR BIVARIATE CIRCULARLY SYMMETRIC SOURCES
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes an algorithm for the design of entropy-constrained unrestricted polar quantizer (ECUPQ) for bivariate circularly symmetric sources. The algorithm is globally optimal for the class of ECUPQs with magnitude quantizer thresholds confined to a finite set. The optimization problem is formulated as the minimization of a weighted sum of the distortion and entropy and the proposed solution is based on modeling the problem as a minimum-weight path problem in a certain weighted directed acyclic graph. The proposed algorithm enables solving the overall problem in
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views
- Read more about PRIMARY-AMBIENT SOURCE SEPARATION FOR UPMIXING TO SURROUNDING SOUND SYSTEMS
- Log in to post comments
Extracting spatial information from an audio recording is a necessary step for upmixing stereo tracks to be played on surround systems. One important spatial feature is the perceived direction of the different audio sources in the recording, which determines how to remix the different sources in the surround system. The focus of this paper is the separation of two types of audio sources: primary (direct) and ambient (surrounding) sources. Several approaches have been proposed to solve the problem, based mainly on the correlation between the two channels in the stereo recording.
- Categories:
 74 Views
74 Views