
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

Uncertainty principles in finite dimensional vector space have been studied extensively, however they cannot be applied to sparse representation of rational functions. This paper considers the sparse representation for a rational function under a pair of orthonormal rational function bases. We prove the uncertainty principle concerning pairs of compressible representation of rational functions in the infinite dimensional function space. The uniqueness of compressible representation using such pairs is provided as a direct consequence of uncertainty principle.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views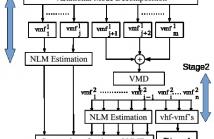
- Read more about EXPLORING THE NON-LOCAL SIMILARITY PRESENT IN VARIATIONAL MODE FUNCTIONS FOR EFFECTIVE ECG DENOISING
- Log in to post comments
In the presented work, noisy ECG signal is decomposed into variational mode functions (VMFs) using variational mode decomposition (VMD) technique. The decomposed VMFs represents the different frequency band of the noisy ECG signal. The non-local similarity present in each VMFs were exploited using NLM estimation for effective ECG denoising. The two-stage VMD decomposition and NLM estimation process is performed on different set of VMFs at both stages. The proposed method is tested upon MIT-BIH Arrhythmia database.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about EXPLORING THE NON-LOCAL SIMILARITY PRESENT IN VARIATIONAL MODE FUNCTIONS FOR EFFECTIVE ECG DENOISING
- Log in to post comments
In the presented work, noisy ECG signal is decomposed into variational mode functions (VMFs) using variational mode decomposition (VMD) technique. The decomposed VMFs represents the different frequency band of the noisy ECG signal. The non-local similarity present in each VMFs were exploited using NLM estimation for effective ECG denoising. The two-stage VMD decomposition and NLM estimation process is performed on different set of VMFs at both stages. The proposed method is tested upon MIT-BIH Arrhythmia database.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about EXPLORING THE NON-LOCAL SIMILARITY PRESENT IN VARIATIONAL MODE FUNCTIONS FOR EFFECTIVE ECG DENOISING
- Log in to post comments
In the presented work, noisy ECG signal is decomposed into variational mode functions (VMFs) using variational mode decomposition (VMD) technique. The decomposed VMFs represents the different frequency band of the noisy ECG signal. The non-local similarity present in each VMFs were exploited using NLM estimation for effective ECG denoising. The two-stage VMD decomposition and NLM estimation process is performed on different set of VMFs at both stages. The proposed method is tested upon MIT-BIH Arrhythmia database.
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views
- Read more about EXPLORING THE NON-LOCAL SIMILARITY PRESENT IN VARIATIONAL MODE FUNCTIONS FOR EFFECTIVE ECG DENOISING
- Log in to post comments
In the presented work, noisy ECG signal is decomposed into variational mode functions (VMFs) using variational mode decomposition (VMD) technique. The decomposed VMFs represents the different frequency band of the noisy ECG signal. The non-local similarity present in each VMFs were exploited using NLM estimation for effective ECG denoising. The two-stage VMD decomposition and NLM estimation process is performed on different set of VMFs at both stages. The proposed method is tested upon MIT-BIH Arrhythmia database.
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views
- Read more about EXPLORING THE NON-LOCAL SIMILARITY PRESENT IN VARIATIONAL MODE FUNCTIONS FOR EFFECTIVE ECG DENOISING
- Log in to post comments
In the presented work, noisy ECG signal is decomposed into variational mode functions (VMFs) using variational mode decomposition (VMD) technique. The decomposed VMFs represents the different frequency band of the noisy ECG signal. The non-local similarity present in each VMFs were exploited using NLM estimation for effective ECG denoising. The two-stage VMD decomposition and NLM estimation process is performed on different set of VMFs at both stages. The proposed method is tested upon MIT-BIH Arrhythmia database.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about CONVOLUTIONAL SEQUENCE TO SEQUENCE MODEL WITH NON-SEQUENTIAL GREEDY DECODING FOR GRAPHEME TO PHONEME CONVERSION
- Log in to post comments
The greedy decoding method used in the conventional sequence-to-sequence models is prone to producing a model with a compounding
of errors, mainly because it makes inferences in a fixed order, regardless of whether or not the model’s previous guesses are correct.
We propose a non-sequential greedy decoding method that generalizes the greedy decoding schemes proposed in the past. The proposed
method determines not only which token to consider, but also which position in the output sequence to infer at each inference step.
- Categories:
 364 Views
364 Views
- Read more about WATCH, LISTEN ONCE, AND SYNC: AUDIO-VISUAL SYNCHRONIZATION WITH MULTI-MODAL REGRESSION CNN
- Log in to post comments
Recovering audio-visual synchronization is an important task in the field of visual speech processing.
- Categories:
 60 Views
60 Views
- Read more about COVER SONG IDENTIFICATION USING SONG-TO-SONG CROSS-SIMILARITY MATRIX WITH CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a cover song identification algorithm using a convolutional neural network (CNN). We first train the CNN model to classify any non-/cover relationship, by feeding a cross-similarity matrix that is generated from a pair of songs as an input. Our main idea is to use the CNN output–the cover-probabilities of one song to all other candidate songs–as a new representation vector for measuring the distance between songs. Based on this, the present algorithm searches cover songs by applying several ranking methods: 1. sorting without using the representation vectors; 2.
- Categories:
 163 Views
163 Views