
- Read more about Cyclic Misspecified Cramer-Rao Bound for Periodic Parameter Estimation
- Log in to post comments
In many practical parameter estimation problems, the observation model is periodic with respect to the unknown parameters. In these cases, the appropriate estimation criterion is periodic in the parameter space, and cyclic performance bounds should be used. However, existing cyclic performance bounds do not account for the common scenario of model misspecification. The misspecified Cramér-Rao bound (MCRB) provides a lower bound on the mean-squared-error (MSE) for estimation problems under model misspecification. However, the MCRB does not provide a valid bound for periodic problems.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
Inference of time-varying data over graphs is of importance in real-world applications such as urban water networks, economics, and brain recordings. It typically relies on identifying a computationally affordable joint spatiotemporal method that can leverage the patterns in the data. While this per se is a challenging task, it becomes even more so when the network comes with uncertainties, which, if not accounted for, can lead to unpredictable consequences.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about A Novel Iterative Thresholding Algorithm for Arctangent Regularization Problem
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we derive the proximity operator of an arctangent penalty, which is expressed using hyperbolic functions of sine and cosine. This penalty is then applied to sparse signal recovery, and an efficient arctangent regularization iterative thresholding (ARIT) algorithm is proposed, offering closed-form solutions for the subproblems associated with the arctangent penalty.
poster_ARIT.pdf
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Joint Multi-Band DOA Estimation Using Low-Rank Matrix Recovery
- Log in to post comments
To address wideband direction of arrival (DOA) estimation problems, this paper proposes a gridless and covariance-free joint multi-band (JMB) DOA estimation method using low-rank matrix recovery. In contrast with subspace methods and sparse array-based methods, a unified frequency grid is established based on the concept of the greatest common divisor (GCD) to solve the nonlinearity of steering matrices from multiple frequencies. With the unified frequency grid, a low-rank master matrix is formed as a combination of the truncated Hankel matrices from different subbands and snapshots.
- Categories:
 127 Views
127 Views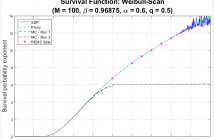
- Read more about New Results on the Weibull Distribution and Weibull Sums, with Application to Radar Sea Clutter
- Log in to post comments
This work covers and combines three themes concerning the Weibull distribution in the heavy-tailed region, as is relevant to sea clutter: (i) Characterizing the Weibull distribution as a compound clutter model and deriving a computationally tractable form for its implied texture distribution. (ii) Computing the distribution of a positively weighted sum of independent identically distributed (iid) Weibull random variables -- facilitated by the compound formulation, with emphasis on the tail.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
As computational tools for X-ray computed tomography (CT) become more quantitatively accurate, knowledge of the source-detector spectral response is critical for quantitative system-independent reconstruction and material characterization capabilities. Directly measuring the spectral response of a CT system is hard, which motivates spectral estimation using transmission data obtained from a collection of known homogeneous objects.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about SIGNAL PROCESSING AND QUANTUM STATE TOMOGRAPHY ON NOISY DEVICES
- Log in to post comments
Quantum State Tomography (QST) is a fundamental tool for quantum signal processing. However, in real noisy quantum devices construction of the state's density matrix via QST can utilize a large amount of resources. Here, we discuss some signal processing techniques that are currently applied to this resource issue, and implement on current quantum chips a modification that can assist in reducing resources. An application of QST to quantum entanglement distillation is provided for further insight.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views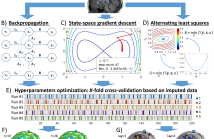
- Read more about DYNAMIC SOURCE LOCALIZATION AND FUNCTIONAL CONNECTIVITY ESTIMATION WITH STATE-SPACE MODELS: PRELIMINARY FEASIBILITY ANALYSIS - Preprint and Code
- Log in to post comments
Dynamic imaging of source and functional connectivity (FC) using electroencephalographic (EEG) signals is essential for understanding the brain and cognition with sufficiently affordable technology to be widely applicable for studying changes associated with healthy ageing and the progression of neuropathology. We present an application for group analysis of recently developed state-space models and algorithms for simultaneously estimating the large-scale EEG inverse and FC problems.
- Categories:
 69 Views
69 Views
- Read more about DYNAMIC SOURCE LOCALIZATION AND FUNCTIONAL CONNECTIVITY ESTIMATION WITH STATE-SPACE MODELS: PRELIMINARY FEASIBILITY ANALYSIS - Poster and Video
- Log in to post comments
Dynamic imaging of source and functional connectivity (FC) using electroencephalographic (EEG) signals is essential for understanding the brain and cognition with sufficiently affordable technology to be widely applicable for studying changes associated with healthy ageing and the progression of neuropathology. We present an application for group analysis of recently developed state-space models and algorithms for simultaneously estimating the large-scale EEG inverse and FC problems.
- Categories:
 113 Views
113 Views
- Read more about Sparse Stable Outlier-Robust Signal Recovery Under Gaussian Noise
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views