
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about NONLINEAR ACOUSTIC ECHO CANCELLATION USING ELITIST RESAMPLING PARTICLE FILTER
- Log in to post comments
This paper considers an effective method for nonlinear acoustic echo cancellation (NL-AEC). More specifically, we model the nonlinear echo path by a latent state vector capturing the coefficients of a memoryless processor and a linear finite impulse response filter. To estimate the posterior probability distribution of the state vector, an elitist particle filter based on evolutionary strategies (EPFES) has been proposed, which evaluates realizations of the latent state vector based on long-term fitness measures.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about NEW MULTI-CARRIER DEMODULATION METHOD APPLIED TO GEARBOX VIBRATION ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about OPTIMAL POOLING OF COVARIANCE MATRIX ESTIMATES ACROSS MULTIPLE CLASSES
- Log in to post comments
The paper considers the problem of estimating the covariance matrices of multiple classes in a low sample support condition, where the data dimensionality is comparable to, or larger than, the sample sizes of the available data sets. In such conditions, a common approach is to shrink the class sample covariance matrices (SCMs) towards the pooled SCM. The success of this approach hinges upon the ability to choose the optimal regularization parameter. Typically, a common regularization level is shared among the classes and determined via a procedure based on cross-validation.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views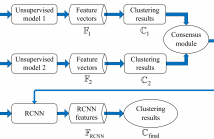
- Read more about PSEUDO-SUPERVISED APPROACH FOR TEXT CLUSTERING BASED ON CONSENSUS ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
In recent years, neural networks (NN) have achieved remarkable
performance improvement in text classification due to
their powerful ability to encode discriminative features by
incorporating label information into model training. Inspired
by the success of NN in text classification, we propose a
pseudo-supervised neural network approach for text clustering.
The neural network is trained in a supervised fashion
with pseudo-labels, which are provided by the cluster labels
of pre-clustering on unsupervised document representations.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about A Simple and Effective Framework for A Priori SNR Estimation
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 88 Views
88 Views
- Read more about L1 PATCH-BASED IMAGE PARTITIONING INTO HOMOGENEOUS TEXTURED REGIONS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views
Counting people automatically in a crowded scenario is important to assess safety and to determine behaviour in surveillance operations. In this paper we propose a new algorithm using the statistics of the spatio-temporal wavelet subbands. A t+2D lifting based wavelet transform is exploited to generate a motion saliency map which is then used to extract novel parametric statistical texture features. We compare our approach to existing crowd counting approaches and show improvement on standard benchmark sequences, demonstrating the robustness of the extracted features.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views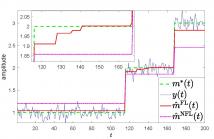
- Read more about CONSISTENT CHANGE POINT DETECTION FOR PIECEWISE CONSTANT SIGNALS WITH NORMALIZED FUSED LASSO
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about SAMPLERNN-BASED NEURAL VOCODER FOR STATISTICAL PARAMETRIC SPEECH SYNTHESIS
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a SampleRNN-based neural vocoder for statistical parametric speech synthesis. This method utilizes a conditional SampleRNN model composed of a hierarchical structure of GRU layers and feed-forward layers to capture long-span dependencies between acoustic features and waveform sequences. Compared with conventional vocoders based on the source-filter model, our proposed vocoder is trained without assumptions derived from the prior knowledge of speech production and is able to provide a better modeling and recovery of phase information.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about SAMPLERNN-BASED NEURAL VOCODER FOR STATISTICAL PARAMETRIC SPEECH SYNTHESIS
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a SampleRNN-based neural vocoder for statistical parametric speech synthesis. This method utilizes a conditional SampleRNN model composed of a hierarchical structure of GRU layers and feed-forward layers to capture long-span dependencies between acoustic features and waveform sequences. Compared with conventional vocoders based on the source-filter model, our proposed vocoder is trained without assumptions derived from the prior knowledge of speech production and is able to provide a better modeling and recovery of phase information.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views