
ICASSP 2021 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2021 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.
- Read more about Towards an ASR Approach Using Acoustic and Language Models for Speech Enhancement
- Log in to post comments
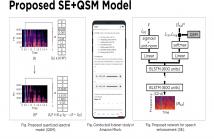
Recent work has shown that deep-learning based speech enhancement performs best when a time-frequency mask is estimated. Unlike speech, these masks have a small range of values that better facilitate regression-based learning. The question remains whether neural-network based speech estimation should be treated as a regression problem. In this work, we propose to modify the speech estimation process, by treating speech enhancement as a classification problem in an ASR-style manner.
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views
Over recent years, deep learning-based computer vision systems have been applied to images at an ever-increasing pace, oftentimes representing the only type of consumption for those images. Given the dramatic explosion in the number of images generated per day, a question arises: how much better would an image codec targeting machine-consumption perform against state-of-the-art codecs targeting human-consumption? In this paper, we propose an image codec for machines which is neural network (NN) based and end-to-end learned.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Processing pipelines for efficient, physically-accurate simulation of microphone array signals in dynamic sound scenes
- Log in to post comments
Multichannel acoustic signal processing is predicated on the fact that the interchannel relationships between the received signals can be exploited to infer information about the acoustic scene. Recently there has been increasing interest in algorithms which are applicable in dynamic scenes, where the source(s) and/or microphone array may be moving. Simulating such scenes has particular challenges which are exacerbated when real-time, listener-in-the-loop evaluation of algorithms is required.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about CNR-IEMN: a deep learning based approach to recognise Covid-19 from CT-scan
- Log in to post comments
SPGC_posterf.pptx
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about TCLA Array: A New Sparse Array Design with Less Mutual Coupling
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about JOINT MASKED CPC AND CTC TRAINING FOR ASR
- Log in to post comments
Self-supervised learning (SSL) has shown promise in learning representations of audio that are useful for automatic speech recognition (ASR). But, training SSL models like wav2vec~2.0 requires a two-stage pipeline. In this paper we demonstrate a single-stage training of ASR models that can utilize both unlabeled and labeled data. During training, we alternately minimize two losses: an unsupervised masked Contrastive Predictive Coding (CPC) loss and the supervised audio-to-text alignment loss Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC).
- Categories:
 120 Views
120 Views
- Read more about ATTACK ON PRACTICAL SPEAKER VERIFICATION SYSTEM USING UNIVERSAL ADVERSARIAL PERTURBATIONS
- Log in to post comments
5375slide.pdf
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
We propose an end-to-end speech synthesizer, Fast DCTTS, that synthesizes speech in real time on a single CPU thread. The proposed model is composed of a carefully-tuned lightweight network designed by applying multiple network reduction and fidelity improvement techniques. In addition, we propose a novel group highway activation that can compromise between computational efficiency and the regularization effect of the gating mechanism. As well, we introduce a new metric called Elastic mel-cepstral distortion (EMCD) to measure the fidelity of the output mel-spectrogram.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Federated Learning With Local Differential Privacy: Trade-Offs Between Privacy, Utility, and Communication
- Log in to post comments
Federated learning (FL) allows to train a massive amount of data privately due to its decentralized structure. Stochastic gradient descent (SGD) is commonly used for FL due to its good empirical performance, but sensitive user information can still be inferred from weight updates shared during FL iterations. We consider Gaussian mechanisms to preserve local differential privacy (LDP) of user data in the FL model with SGD. The trade-offs between user privacy, global utility, and transmission rate are proved by defining appropriate metrics for FL with LDP.
- Categories:
 68 Views
68 Views