
- Read more about Poster for the paper "Buffered Gaussian Modeling For Vectorized HD Map Construction"
- Log in to post comments
Vectorized high-definition (HD) map construction is an important and challenging task for autonomous driving. End-to-end models have been developed recently to enable online map construction. Existing works have difficulty in generating complex geometric shapes and lack comprehensive evaluation metrics. To tackle these challenges, we introduce buffered IoU as a novel metric for vectorized map construction, which is clearly defined and applicable to real-world situations. Inspired by methods of rotated object detection, we further propose a novel technique called Buffered Gaussian Modeling.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about MULTI-LEVEL CONTRASTIVE LEARNING FOR HYBRID CROSS-MODAL RETRIEVAL
- Log in to post comments
Hybrid image retrieval is a significant task for a wide range of applications. In this scenario, the hybrid query for searching images consists of a reference image and a text modifier. The reference image provides a vital visual context and displays some semantic details, while the text modifier specifies the modifications to the reference image. To address such hybrid cross-modal retrieval, we propose a multi-level contrastive learning (MLCL) method for combining the hybrid query features into a fused feature by cross-modal contrastive learning with multi-level semantic alignment.
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views
Versatile Video Coding (VVC) now supports Screen Content Coding (SCC) by integrating two efficient coding modes: Intra Block Copy (IBC) and Palette (PLT). However, the numerous
modes and the Quad-Tree Plus Multi-Type Tree (QTMT) structure inherent to VVC contribute to a very high coding complexity. To effectively reduce the computational complexity
of VVC SCC, we propose a fast Intra mode prediction algorithm for VVC SCC. More specifically, we first use the difference of minimum Sum of Absolute Transformed Differences
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views
- Read more about Learned Video Compression with Spatial-Temporal Optimization
- Log in to post comments
Previous optical flow based video compression is gradually replaced by unsupervised deformable convolution (DCN) based method. This is mainly due to the fact that the motion vector (MV) estimated by the existing optical flow network
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about RD-COST REGRESSION SPEED UP TECHNIQUE FOR VVC INTRA BLOCK PARTITIONING
- Log in to post comments
The last standard Versatile Video Codec (VVC) aims to improve the compression efficiency by saving around 50% of bitrate at the same quality compared to its predecessor High Efficiency Video Codec (HEVC). However, this comes with higher encoding complexity mainly due to a much larger number of block splits to be tested on the encoder side.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Extreme low bitrate Image Compression system for mobile deployment
- Log in to post comments
End-to-end image compression has achieved satisfactory results in recent years. However, existing methods suffer from the high complexity of complicated neural networks and cannot be directly deployed on mobile devices due to the limitations of computation and storage. Therefore, considering the resource and computing ability constrains of the mobile devices, we make a trade-off in this paper between rate-distortion (R-D) performance, inference time, and model complexity.
Manuscript.pdf
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views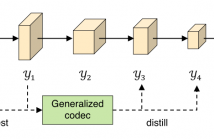
- Read more about Visual Coding for Humans and Machines
- Log in to post comments
Visual content is increasingly being used for more than human viewing. For example, traffic video is automatically analyzed to count vehicles, detect traffic violations, estimate traffic intensity, and recognize license plates; images uploaded to social media are automatically analyzed to detect and recognize people, organize images into thematic collections, and so on; visual sensors on autonomous vehicles analyze captured signals to help the vehicle navigate, avoid obstacles, collisions, and optimize their movement.
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
- Read more about Standard Compliant Video Coding using Low Complexity, Switchable Neural Wrappers: Supplementary Material
- Log in to post comments
This supplementary material presents detailed experimental results for ICIP 2024 submission titled "Standard Compliant Video Coding using Low Complexity, Switchable Neural Wrappers".
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about SALIENCY-AWARE END-TO-END LEARNED VARIABLE-BITRATE 360-DEGREE IMAGE COMPRESSION SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
- Log in to post comments
Effective compression of 360-degree images, also referred to as omnidirectional images (ODIs), is of high interest for various virtual reality (VR) and related applications. 2D image compression methods ignore the equator-biased nature of ODIs and fail to address oversampling near the poles, leading to inefficient compression when applied to ODI. We present a new learned saliency-aware 360-degree image compression architecture that prioritizes bit allocation to more significant regions, considering the unique properties of ODIs.
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
- Read more about AudioVMAF: Audio Quality Prediction with VMAF
- Log in to post comments
Video Multimethod Assessment Fusion (VMAF) [1],[2],[3] is a popular tool in the industry for measuring coded video quality. In this study, we propose an auditory-inspired frontend in existing VMAF for creating videos of reference and coded spectrograms, and extended VMAF for measuring coded audio quality. We name our system AudioVMAF. We demonstrate that image replication is capable of further enhancing prediction accuracy, especially when band-limited anchors are present.
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views