
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about TOWARDS A GENERIC COMPRESSION SOLUTION FOR DENSELY AND SPARSELY SAMPLED LIGHT FIELD DATA
- Log in to post comments
Light field acquisition technologies capture spatial and angular information of the scene. The angular information paves
the way for various post-processing applications, e.g. scene reconstruction, refocusing, synthetic aperture. The light field
is usually captured by a single plenoptic camera or by multiple traditional cameras. The former captures dense light
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about RESIDUAL SIGNALS MODELING FOR LAYERED IMAGE/VIDEO SOFTCAST WITH HYBRID DIGITAL-ANALOG TRANSMISSION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views

- Read more about An Interior Point Method for Nonnegative Sparse Signal Reconstruction
- Log in to post comments
We present a primal-dual interior point method (IPM) with a novel preconditioner to solve the ℓ1-norm regularized least square problem for nonnegative sparse signal reconstruction. IPM is a second-order method that uses both gradient and Hessian information to compute effective search directions and achieve super-linear convergence rates. It therefore requires many fewer iterations than first-order methods such as iterative shrinkage/thresholding algorithms (ISTA) that only achieve sub-linear convergence rates.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about A NOVEL CONFIDENCE MEASURE FOR DISPARITY MAPS BY PIXEL-WISE COST FUNCTION ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Read more about UNIFORM EMBEDDING FOR EFFICIENT STEGANOGRAPHY OF H.264 VIDEO
- Log in to post comments
ICIP海报.pdf
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about A-CCNN: Adaptive CCNN for Density Estimation and Crowd Counting
- Log in to post comments
Crowd counting, for estimating the number of people in a crowd using vision-based computer techniques, has attracted much interest in the research community. Although many attempts have been reported, real-world problems, such as huge variation in subjects’ sizes in images and serious occlusion among people, make it still a challenging problem. In this paper, we propose an Adaptive Counting Convolutional Neural Network (A-CCNN) and consider the scale variation of objects in a frame adaptively so as to improve the accuracy of counting.
ICIP2018.pptx
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views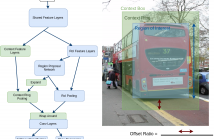
- Read more about IMPROVING PROPOSAL-BASED OBJECT DETECTION USING CONVOLUTIONAL CONTEXT FEATURES
- Log in to post comments
A novel extension to proposal-based detection is proposed in order to learn convolutional context features for determining boundaries of objects better. Objects and their context are aimed to be learned through parallel convolutional stages. The resulting object and context feature maps are combined in such a way that they preserve their spatial relationship. The proposed algorithm is trained and evaluated on PASCAL VOC 2007 detection benchmark dataset and yielded improvements in performance over baseline, for all classes, especially the ones with distinctive context.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views