
Deep learning-based methods provide remarkable performance in a number of computational imaging problems. Examples include end-to-end trained networks that map measurements to unknown signals, plug-and-play (PnP) methods that use pretrained denoisers as image prior, and model-based unrolled networks that train artifact removal blocks. Many of these methods lack robustness and fail to generalize with distribution shifts in data, measurements, and noise. In this paper, we present a simple framework to perform domain adaptation as data and measurement distribution shifts.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about Beyond the Limit of Weight-Sharing: Pioneering Space-Evolving NAS with Large Language Models
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Large language models (LLMs) offer impressive performance across diverse fields, but their increasing complexity raises both design costs and the need for specialized expertise. These challenges are intensified for Neural Architecture Search (NAS) methods reliant on weight-sharing techniques. This paper introduces GNAS, a new NAS method that boosts the search process with the aid of LLMs for efficient model discovery. With insights from existing architectures, GNAS swiftly identifies superior models that can adapt to changing resource constraints.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about 3D POSE ESTIMATION FROM MONOCULAR VIDEO WITH CAMERA-BONE ANGLE REGULARIZATION ON THE IMAGE FEATURE
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a monocular 3D pose estimation method which explicitly takes into account the angles between the camera optical axis and bones (camera-bone angles) as well as temporal information. The proposed method combines a 2D-to-3D-based method, which predicts a 3D pose from a sequence of 2D poses, and convolutional neural network (CNN) and includes novel regularization loss to enable the CNN to extract camera-bone-angle information.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views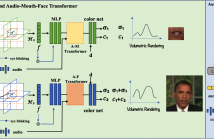
- Read more about DT-NeRF: Decomposed Triplane-Hash Neural Radiance Fields for High-Fidelity Talking Portrait Synthesis
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present the decomposed triplane-hash neural radiance fields (DT-NeRF), a framework that significantly improves the photorealistic rendering of talking faces and achieves state-of-the-art results on key evaluation datasets. Our architecture decomposes the facial region into two specialized triplanes: one specialized for representing the mouth, and the other for the broader facial features. We introduce audio features as residual terms and integrate them as query vectors into our model through an audio-mouthface transformer.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about DYNAMIC VIDEO FRAME INTERPOLATION WITH INTEGRATED DIFFICULTY PRE-ASSESSMENT
- Log in to post comments
Video frame interpolation (VFI) has witnessed great progress in recent years. However, existing VFI models still struggle to achieve a good trade-off between accuracy and efficiency. Accurate VFI models typically rely on heavy compute to process all samples, ignoring the fact that easy samples with small motion or clear texture can be well addressed by a fast VFI model and do not require such heavy compute. In this paper, we present a dynamic VFI pipeline with integrated pre-assessment of interpolation difficulty.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Supplementing Missing Visions via Dialog for Scene Graph Generations
- Log in to post comments
Most AI systems rely on the premise that the input visual data are sufficient to achieve competitive performance in various tasks. However, the classic task setup rarely considers the challenging, yet common practical situations where the complete visual data may be inaccessible due to various reasons (e.g., restricted view range and occlusions). To this end, we investigate a task setting with incomplete visual input data. Specifically, we exploit the Scene Graph Generation (SGG) task with various levels of visual data missingness as input.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about Photovoltaic power forecasting using sky images and sun motion
- Log in to post comments
Solar energy adoption is moving at a rapid pace. The variability in solar energy production causes grid stability issues and hinders mass adoption. To solve these issues, more accurate photovoltaic power forecasting systems are needed. In intra-hour forecasting, the most challenging issue is high output fluctuations due to cloud motion, which can occlude the sun.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about PROBMCL: SIMPLE PROBABILISTIC CONTRASTIVE LEARNING FOR MULTI-LABEL VISUAL CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
Multi-label image classification presents a challenging task in many domains, including computer vision and medical imaging. Recent advancements have introduced graph-based and transformer-based methods to improve performance and capture label dependencies. However, these methods often include complex modules that entail heavy computation and lack interpretability. In this paper, we propose Probabilistic Multi-label Contrastive Learning (ProbMCL), a novel framework to address these challenges in multi-label image classification tasks.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Self-Supervised Face Image Restoration with a One-Shot Reference
- Log in to post comments
For image restoration, methods leveraging priors from generative models have been proposed and demonstrated a promising capacity to robustly restore photorealistic and high-quality results. However, these methods are susceptible to semantic ambiguity, particularly with images that have obviously correct semantics, such as facial images. In this paper, we propose a semantic-aware latent space exploration method for image restoration (SAIR).
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views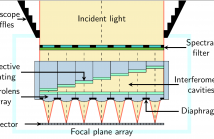
- Read more about Spectro-spatial hyperspectral image reconstruction from interferometric acquisitions
- Log in to post comments
In the last decade, novel hyperspectral cameras have been developed with particularly desirable characteristics of compactness and short acquisition time, retaining their potential to obtain spectral/spatial resolution competitive with respect to traditional cameras. However, a computational effort is required to recover an interpretable data cube.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views