- Read more about CSfM: Community-based Structure-from-Motion
- Log in to post comments
Structure-from-Motion approaches could be broadly divided into two classes: incremental and global. While incremental manner is robust to outliers, it suffers from error accumulation and heavy computation load. The global manner has the advantage of simultaneously estimating all camera poses, but it is usually sensitive to epipolar geometry outliers. In this paper, we propose an adaptive community-based SfM (CSfM) method which takes both robustness and efficiency into consideration. First, the epipolar geometry graph is partitioned into separate communities.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views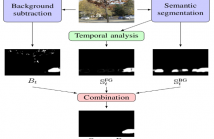
- Read more about Semantic Background Subtraction
- Log in to post comments
We introduce the notion of semantic background subtraction, a novel framework for motion detection in video sequences. The key innovation consists to leverage object-level semantics to address the variety of challenging scenarios for background subtraction. Our framework combines the information of a semantic segmentation algorithm, expressed by a probability for each pixel, with the output of any background subtraction algorithm to reduce false positive detections produced by illumination changes, dynamic backgrounds, strong shadows, and ghosts.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views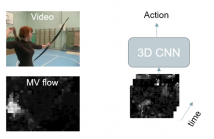
- Read more about COMPRESSED-DOMAIN VIDEO CLASSIFICATION WITH DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS: “THERE’S WAY TOO MUCH INFORMATION TO DECODE THE MATRIX”
- Log in to post comments
We investigate video classification via a 3D deep convolutional neural network (CNN) that directly ingests compressed bitstream information. This idea is based on the observation that video macroblock (MB) motion vectors (that are very compact and directly available from the compressed bitstream) are inherently capturing local spatiotemporal changes in each video scene.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views- Read more about Convolutional Neural Networks and Training Strategies for Skin Detection
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views- Read more about MOTION-CONSISTENT VIDEO INPAINTING
- Log in to post comments
This project aims to propose a fast and automatic inpainting technique for high-definition videos which works under many challenging conditions such as a moving camera, a dynamic background or a long occlusion. Our algorithm does not limit to objects removal type but extends to simultaneous background and foreground reconstruction even when the moving objects are occluded for a long period. Built upon Newson et al [1] which optimizes a global patch-based function, our method holds a significant improvement by the introduction of the optical flow term.
final.pptx
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about MOTION-CONSISTENT VIDEO INPAINTING
- Log in to post comments
This demonstration aims to show some resulting videos for our method presented in ICIP. It is a fast and automatic inpainting technique for high-definition videos which works under many challenging conditions such as a moving camera, a dynamic background or a long-lasting occlusion. By incorporating optical flow in a global patch-based algorithm, our method provide improvements compared to the state-of-the-art, especially in motion preservation.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views- Read more about MOTION-CONSISTENT VIDEO INPAINTING
- Log in to post comments
This demonstration aims to show some resulting videos for our method presented in ICIP. It is a fast and automatic inpainting technique for high-definition videos which works under many challenging conditions such as a moving camera, a dynamic background or a long-lasting occlusion. By incorporating optical flow in a global patch-based algorithm, our method provide improvements compared to the state-of-the-art, especially in motion preservation.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views- Read more about ROBUST SYNTHETIC BASIS FEATURE DESCRIPTOR
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views- Read more about Semantic Segmentation with Multi-path Refinement and Pyramid Pooling Dilated-Resnet
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about MUSeed: A Mobile Image Analysis Application for Plant Seed Morphometry
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views