
- Read more about ON COMPRESSIVE SENSING OF SPARSE COVARIANCE MATRICES USING DETERMINISTIC SENSING MATRICES
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about On the Role of the Bounded Lemma in the SDP Formulation of Atomic Norm Problems
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 84 Views
84 Views
- Read more about Bandlimited Spatiotemporal Field Sampling with Location and Time Unaware Mobile Sensors
- Log in to post comments
Sampling of smooth spatiotemporally varying fields is a well studied topic in the literature. Classical approach assumes that the field is observed at known sampling locations and known timestamps ensuring field reconstruction. In a first, in this work the sampling and reconstruction of a spatiotemporal bandlimited field is addressed, where the samples are obtained by a location-unaware, time-unaware mobile sensor. The spatial and temporal order of samples is assumed to be known. It is assumed that the field samples are affected by measurement-noise.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views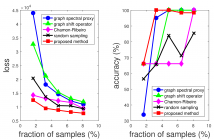
- Read more about On the Supermodularity of Active Graph-based Semi-supervised Learning with Stieltjes Matrix Regularization
- Log in to post comments
Active graph-based semi-supervised learning (AG-SSL) aims to select a small set of labeled examples and utilize their graph-based relation to other unlabeled examples to aid in machine learning tasks. It is also closely related to the sampling theory in graph signal processing. In this paper, we revisit the original formulation of graph-based SSL and prove the supermodularity of an AG-SSL objective function under a broad class of regularization functions parameterized by Stieltjes matrices.
- Categories:
 83 Views
83 Views
In this work, we introduce subset selection strategies for signal reconstruction based on kernel methods, particularly for the case of kernel-ridge regression. Typically, these methods are employed for exploiting known prior information about the structure of the signal of interest. We use the mean squared error and a scalar function of the covariance matrix of the kernel regressors to establish metrics for the subset selection problem. Despite the NP-hard nature of the problem, we introduce efficient algorithms for finding approximate solutions for the proposed metrics.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views

- Read more about Recovery of noisy points on band-limited surfaces
- Log in to post comments
We introduce a continuous domain framework for the recovery of points on a surface in high dimensional space, represented as the zero-level set of a bandlimited function. We show that the exponential maps of the points on the surface satisfy annihilation relations, implying that they lie in a finite dimensional subspace. The subspace properties are used to derive sampling conditions, which will guarantee the perfect recovery of the surface from finite number of points.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about DESIGN OF OPTIMAL ENTROPY-CONSTRAINED UNRESTRICTED POLAR QUANTIZER FOR BIVARIATE CIRCULARLY SYMMETRIC SOURCES
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes an algorithm for the design of entropy-constrained unrestricted polar quantizer (ECUPQ) for bivariate circularly symmetric sources. The algorithm is globally optimal for the class of ECUPQs with magnitude quantizer thresholds confined to a finite set. The optimization problem is formulated as the minimization of a weighted sum of the distortion and entropy and the proposed solution is based on modeling the problem as a minimum-weight path problem in a certain weighted directed acyclic graph. The proposed algorithm enables solving the overall problem in
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views