
- Read more about An Analysis of Speech Enhancement and Recognition Losses in Limited Resources Multi-Talker Single Channel Audio-Visual ASR
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we analyzed how audio-visual speech enhancement can help to perform the ASR task in a cocktail party scenario. Therefore we considered two simple end-to-end LSTM-based models that perform single-channel audiovisual speech enhancement and phone recognition respectively. Then, we studied how the two models interact, and how to train them jointly affects the final result.We analyzed different training strategies that reveal some interesting and unexpected behaviors.
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views
- Categories:
 79 Views
79 Views
- Read more about SPECTROGRAMS FUSION WITH MINIMUM DIFFERENCE MASKS ESTIMATION FOR MONAURAL SPEECH DEREVERBERATION
- Log in to post comments
Spectrograms fusion is an effective method for incorporating complementary speech dereverberation systems. Previous linear spectrograms fusion by averaging multiple spectrograms shows outstanding performance. However, various systems with different features cannot apply this simple method. In this study, we design the minimum difference masks (MDMs) to classify the time-frequency (T-F) bins in spectrograms according to the nearest distances from labels. Then, we propose a two-stage nonlinear spectrograms fusion system for speech dereverberation.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
- Read more about ICASSP 2019 Paper #4001: INCREASE APPARENT PUBLIC SPEAKING FLUENCY BY SPEECH AUGMENTATION
- Log in to post comments
Fluent and confident speech is desirable to every speaker. But professional speech delivering requires a great deal of experience and practice. In this paper, we propose a speech stream manipulation system which can help non-professional speakers to produce fluent, professional-like speech content, in turn contributing towards better listener engagement and comprehension. We propose to achieve this task by manipulating the disfluencies in human speech, like the sounds uh and um, the filler words and awkward long silences.
- Categories:
 71 Views
71 Views
- Read more about Learning to Dequantize Speech Signals by Primal-Dual Networks: An Approach for Acoustic Sensor Networks
- Log in to post comments
We introduce a method to improve the quality of simple scalar quantization in the context of acoustic sensor networks by combining ideas from sparse reconstruction, artificial neural networks and weighting filters. We start from the observation that optimization methods based on sparse reconstruction resemble the structure of a neural network. Hence, building upon a successful enhancement method, we unroll the algorithms and use this to build a neural network which we train to obtain enhanced decoding.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Incremental Binarization On Recurrent Neural Networks For Single-Channel Source Separation
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a Bitwise Gated Recurrent Unit (BGRU) network for the single-channel source separation task. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) require several sets of weights within its cells, which significantly increases the computational cost compared to the fully-connected networks. To mitigate this increased computation, we focus on the GRU cells and quantize the feedforward procedure with binarized values and bitwise operations. The BGRU network is trained in two stages.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views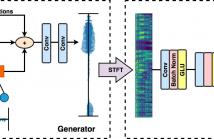
- Read more about Perceptually-motivated environment-specific speech enhancement
- Log in to post comments
This paper introduces a deep learning approach to enhance speech recordings made in a specific environment. A single neural network learns to ameliorate several types of recording artifacts, including noise, reverberation, and non-linear equalization. The method relies on a new perceptual loss function that combines adversarial loss with spectrogram features. Both subjective and objective evaluations show that the proposed approach improves on state-of-the-art baseline methods.
- Categories:
 68 Views
68 Views
- Read more about Face Landmark-based Speaker-Independent Audio-Visual Speech Enhancement in Multi-Talker Environments
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we address the problem of enhancing the speech of a speaker of interest in a cocktail party scenario when visual information of the speaker of interest is available.Contrary to most previous studies, we do not learn visual features on the typically small audio-visual datasets, but use an already available face landmark detector (trained on a separate image dataset).The landmarks are used by LSTM-based models to generate time-frequency masks which are applied to the acoustic mixed-speech spectrogram.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Using recurrences in time and frequency within U-net architecture for speech enhancement
- Log in to post comments
When designing fully-convolutional neural network, there is a trade-off between receptive field size, number of parameters and spatial resolution of features in deeper layers of the network. In this work we present a novel network design based on combination of many convolutional and recurrent layers that solves these dilemmas. We compare our solution with U-nets based models known from the literature and other baseline models on speech enhancement task.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Artificial Bandwidth Extension of Narrowband Speech Using Generative Adversarial Networks
- Log in to post comments
The aim of artificial bandwidth extension is to recreate wideband speech (0 - 8 kHz) from a narrowband speech signal (0 - 4 kHz). State-of-the-art approaches use neural networks for this task. As a loss function during training, they employ the mean squared error between true and estimated wideband spectra. This, however, comes with the drawback of over-smoothing, which expresses itself in strongly underestimated dynamics of the upper frequency band.
- Categories:
 174 Views
174 Views