- Read more about SPEECH DEREVERBERATION USING NMF WITH REGULARIZED ROOM IMPULSE RESPONSE
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, various regularizations on the room impulse response
(RIR) are proposed to obtain better single-channel speech derever-
beration in the non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) framework.
The regularizations on the RIR are motivated by the spectral domain
representation of the RIR. To obtain better estimates of the RIR and
clean speech, we propose three modifications (i) to obtain a sparse
RIR (ii) a frequency envelop constrained RIR and (iii) to include the
early part of the RIR. The performance of the proposed regularizers
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views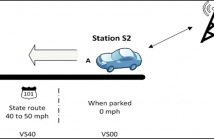
- Read more about A QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF HANDS-FREE SPEECH ENHANCEMENT USING REAL AUTOMOBILE DATA
- Log in to post comments
This paper provides a detailed comparison study between three different vehicles’ Bluetooth built-in noise cancellation filter with two widely used techniques in speech enhancement, Spectral Subtraction (SS) and Wiener filtering (WF). The main purpose is to determine if any of these two filters provide superior audio quality over the built-in filter.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views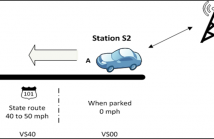
- Read more about A QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF HANDS-FREE SPEECH ENHANCEMENT USING REAL AUTOMOBILE DATA
- Log in to post comments
This paper provides a detailed comparison study between three different vehicles’ Bluetooth built-in noise cancellation filter with two widely used techniques in speech enhancement, Spectral Subtraction (SS) and Wiener filtering (WF). The main purpose is to determine if any of these two filters provide superior audio quality over the built-in filter.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views- Read more about Deep Neural Network for Robust Speech Recognition With Auxiliary Features From Laser-Doppler Vibrometer Sensor
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about Dual-microphone voice activity detection based on using optimally weighted maximum a posteriori probability
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views- Read more about System-Compatible Robustness Improvement for New Generation DECT Decoders by G.722 Soft-Decision Decoding
- Log in to post comments
The ITU-T Recommendation G.722 about subband adaptive differential pulse code modulation (SB-ADPCM) is the mandatory wideband speech codec in the new generation digital enhanced cordless telephony (NG-DECT). Although in ADPCM the difference signal instead of the original signal is quantized and adaptive prediction is employed, redundancy is yet observed within the quantized samples. In this paper we apply a soft-decision speech decoding technique which exploits this redundancy in terms of a priori knowledge and the channel reliability information to NG-DECT.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about Sparse Reconstruction of Quantized Speech Signals
- Log in to post comments
We propose sparse reconstruction techniques to improve the quality and / or reduce the bit-rate of standard speech coders. To that end, we assume signal sparsity in some transform domain and formulate the problem of reconstructing the original signal in terms of constrained l1-norm minimization. We use modern primal-dual methods in order to solve the resulting non-smooth convex optimization problem. Experiments show that with the proposed sparse reconstruction method the instrumentally predicted speech quality can be largely improved.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about Multiplicative Update of AR gains in Codebook-driven Speech Enhancement
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views- Read more about USING CONDITIONAL RESTRICTED BOLTZMANN MACHINES FOR SPECTRAL ENVELOPE MODELING IN SPEECH BANDWIDTH EXTENSION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views