Documents
Presentation Slides
Theoretical Performance Bound of Uplink Channel Estimation Accuracy in Massive MIMO
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Alexander Osinsky
- Last updated:
- 14 May 2020 - 5:26am
- Document Type:
- Presentation Slides
- Document Year:
- 2020
- Event:
- Presenters:
- Alexander Osinsky
- Paper Code:
- SAM-P6.5
- Categories:
- Log in to post comments
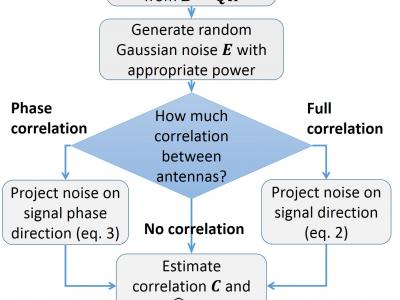
In this paper, we present a new performance bound for uplink channel estimation (CE) accuracy in the Massive Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) system. The proposed approach is based on noise power calculation after the CE unit in a multi-antenna receiver. Each time the impulse response of ideal channel estimation is decomposed into separate taps (beams) and cross-covariance matrix is calculated between them. Then a linear minimum mean squared error (MMSE) method is applied with these taps to estimate the value of residual CE error power for each unique scenario, assuming Gaussian distribution of tap amplitudes and antennas noise. An artificial CE is calculated as a sum of ideal CE (pre-defined Quadriga model) and additive Gaussian noise with the same error power. The artificial CE is then utilized in MIMO detector and decoder units to calculate performance bound. Our method outperforms the accuracy of a well-known Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) due to considering more statistics since performance strongly depends on a number of channel taps and power ratio between them. Simulation results are presented for the non-line of sight 3D-UMa model of 5G QuaDRiGa 2.0 channel and compared with the generalized CRLB and state-of-the-art CE algorithms.

