
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about MODELING NON-LINGUISTIC CONTEXTUAL SIGNALS IN LSTM LANGUAGE MODELS VIA DOMAIN ADAPTATION
- Log in to post comments
When it comes to speech recognition for voice search, it would be
advantageous to take into account application information associated
with speech queries. However, in practice, the vast majority
of queries typically lack such annotations, posing a challenge to
train domain-specific language models (LMs). To obtain robust domain
LMs, typically a LM which has been pre-trained on general
data will be adapted to specific domains. We propose four adaptation
schemes to improve the domain performance of long shortterm
domain.pdf
- Categories:
 94 Views
94 Views
- Read more about ADAPTIVE CLUSTERING ALGORITHM FOR COOPERATIVE SPECTRUM SENSING IN MOBILE ENVIRONMENTS
- Log in to post comments
In this work we propose a new adaptive algorithm for coop- erative spectrum sensing in dynamic environments where the channels are time varying. We assume a centralized spectrum sensing procedure based on the soft fusion of the signal energy levels measured at the sensors. The detection problem is posed as a composite hypothesis testing problem. The unknown pa- rameters are estimated by means of an adaptive clustering al- gorithm that operates over the most recent energy estimates re- ported by the sensors to the fusion center.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Cross-Modality Distillation: A Case for Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose to use a Conditional Generative Adversarial Network (CGAN) for distilling (i.e. transferring) knowledge from sensor data and enhancing low-resolution target detection. In unconstrained surveillance settings, sensor measurements are often noisy, degraded, corrupted, and even missing/absent, thereby presenting a significant problem for multi-modal fusion. We therefore specifically tackle the problem of a missing modality in our attempt to propose an algorithm
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views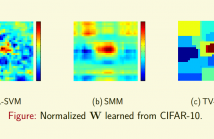
- Read more about TV-SVM: Support Vector Machine with Total Variational Regularization
- Log in to post comments
To leverage the spatial relationship of lattice data, such as images, we introduce total variational (TV) regularization into support vector machines (SVM), called TV-SVM. TV-SVM encourages local smoothness and sparsity in gradient domain of the learned parameters. TV-SVM is optimized via the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) algorithm and is significantly better than (Linear) SVM for image classifications.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about A Refined Analysis of the Gap between Expected Rate for Partial CSIT and the Massive MIMO Rate Limit
- Log in to post comments
Optimal BeamFormers (BFs) that maximize the Weighted Sum Rate
(WSR) for a Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) interference
broadcast channel (IBC) remains an important research area. Under
practical scenarios, the problem is compounded by the fact that only
partial channel state information at the transmitter (CSIT) is available.
Hence, a typical choice of the optimization metric is the Expected
Weighted Sum Rate (EWSR). However, the presence of the
expectation operator makes the optimization a daunting task. On the
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views
- Read more about Verbal Protest Recognition in Children with Autism
- Log in to post comments
Real-time detection of verbal protest (sensory overload-induced crying) in children with autism is a first step towards understanding the precursors of challenging behaviors associated with autism. Detection of verbal protest is useful for both autism researchers interested in exploring just-in-time intervention techniques and researchers interested in audio event detection in routine living environments.In this paper, we examine, adapt, and improve upon two techniques for verbal protest recognition and tailor them for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
- Categories:
 243 Views
243 Views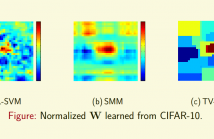
- Read more about TV-SVM: Support Vector Machine with Total Variational Regularization
- Log in to post comments
To leverage the spatial relationship of lattice data, such as images, we introduce total variational (TV) regularization into support vector machines (SVM), called TV-SVM. TV-SVM encourages local smoothness and sparsity in gradient domain of the learned parameters. TV-SVM is optimized via the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) algorithm and is significantly better than (Linear) SVM for image classifications.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views
- Read more about Optimal algorithms and CRB for reciprocity calibration in Massive MIMO
- Log in to post comments
Gains from Massive MIMO are crucially dependent on the availability
of channel state information at the transmitter which is far
too costly if it has to estimated directly. Hence, for a time division
duplexing system, this is derived from the uplink channel estimates
using the concept of channel reciprocity. However, while the propagation
channel is reciprocal, the overall digital channel in the downlink
also involves the radio frequency chain which is non-reciprocal.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views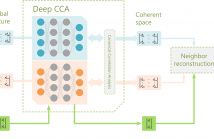
- Read more about LOW RESOLUTION FACE RECOGNITION AND RECONSTRUCTION VIA DEEP CANONICAL CORRELATION ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
Low-resolution (LR) face identification is always a challenge in computer vision. In this paper, we propose a new LR face recognition and reconstruction method using deep canonical correlation analysis (DCCA). Unlike linear CCA-based methods, our proposed method can learn flexible nonlinear representations by passing LR and high-resolution (HR) image principal component features through multiple stacked layers of nonlinear transformation.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views