
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about automatic segmentation and cardiopathy classification in cardiac MRI images based on deep neural networks
- Log in to post comments
Segmentation of cardiac MRI images plays a key role in clinical diagnosis. In the traditional diagnostic process, clinical experts manually segment left ventricle (LV), right ventricle (RV) and myocardium to obtain guideline for cardiopathy diagnosis. However, manual segmentation is time-consuming and labor-intensive. In this paper, we propose automatic segmentation and cardiopathy classification in cardiac MRI images
based on deep neural networks. First, we perform object detection based on a YOLO-based network to get region of interest
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views
- Read more about UNOBTRUSIVE MONITORING OF SPEECH IMPAIRMENTS OF PARKINSON'S DISEASE PATIENTS THROUGH MOBILE DEVICES
- Log in to post comments
Parkinson’s disease (PD) produces several speech impairments in the patients. Automatic classification of PD patients is performed considering speech recordings collected in non- controlled acoustic conditions during normal phone calls in a unobtrusive way. A speech enhancement algorithm is applied to improve the quality of the signals. Two different classification approaches are considered: the classification of PD patients and healthy speakers and a multi-class experiment to classify patients in several stages of the disease.
icassp.pdf
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views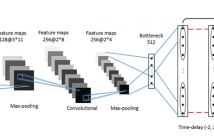
- Read more about Human and Machine Speaker Recognition on Short Trivial Events
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we collect a trivial event speech database that involves 75 speakers and 6 types of events, and report preliminary speaker recognition results on this database, by both human listeners and machines. Particularly, the deep feature learning technique recently proposed by our group is utilized to analyze and recognize the trivial events, leading to acceptable equal error rates (EERs) ranging from 5% to 15% despite the extremely short durations (0.2-0.5 seconds) of these events. Comparing different types of events, ‘hmm’ seems more speaker discriminative.
trivial.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about Human and Machine Speaker Recognition on Short Trivial Events
- Log in to post comments
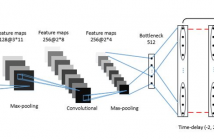
In this paper, we collect a trivial event speech database that involves 75 speakers and 6 types of events, and report preliminary speaker recognition results on this database, by both human listeners and machines. Particularly, the deep feature learning technique recently proposed by our group is utilized to analyze and recognize the trivial events, leading to acceptable equal error rates (EERs) ranging from 5% to 15% despite the extremely short durations (0.2-0.5 seconds) of these events. Comparing different types of events, ‘hmm’ seems more speaker discriminative.
trivial.pdf
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Optimal Tone Reservation for Peak to Average Power Control of CDMA Systems
- Log in to post comments
In this paper we study the tone reservation technique for the reduction of the peak to average power ratio (PAPR) in code division multiple access (CDMA) systems that employ the Walsh functions. In the tone reservation method, the available carriers are partitioned into two sets, the information set, which carries the information, and the compensation set, which is used to reduce the PAPR. Central questions are: What is the best possible reduction of the PAPR? What is the optimal information set that achieves this reduction, and how can it be found?
- Categories:
 67 Views
67 Views
A method to create multipoles comprising a cluster of focused sources by using a linear loudspeaker array has recently been investigated. Directivities in a listening area were confirmed with examples of primitive multipoles such as dipoles and quadrupoles. This paper describes a method to create a sound source having more complex directivity by using a superposition of multipoles comprising a collection of focused sources.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views
- Read more about STATISTICAL EVALUATION OF VISUAL QUALITY METRICS FOR IMAGE DENOISING
- Log in to post comments
This paper studies the problem of full reference visual quality assessment of denoised images with a special emphasis on images with low contrast and noise-like texture. Denoising of such images together with noise removal often results in image details loss or smoothing. A new test image database, FLT, containing 75 noise-free ‘reference’ images and 300 filtered (‘distorted’) images is developed. Each reference image, corrupted by an additive white Gaussian noise, is denoised by the BM3D filter with four different values of threshold parameter (four levels of noise suppression).
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about REINFORCEMENT LEARNING OF SPEECH RECOGNITION SYSTEM BASED ON POLICY GRADIENT AND HYPOTHESIS SELECTION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views