
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Joint License Plate Super-Resolution and Recognition in One Multi-Task GAN Framework
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views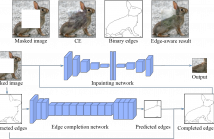
- Read more about Edge-aware Context Encoder for Image Inpainting
- Log in to post comments
We present Edge-aware Context Encoder (E-CE): an image inpainting model which takes scene structure and context into account. Unlike previous CE which predicts the missing regions using context from entire image, E-CE learns to recover the texture according to edge structures, attempting to avoid context blending across boundaries. In our approach, edges are extracted from the masked image, and completed by a full-convolutional network. The completed edge map together with the original masked image are then input into the modified CE network to predict the missing region.
- Categories:
 260 Views
260 Views
- Read more about Attention-based Dialog State Tracking for Conversational Interview Coaching
- Log in to post comments
This study proposes an approach to dialog state tracking (DST) in a conversational interview coaching system. For the interview coaching task, the semantic slots, used mostly in traditional dialog systems, are difficult to define manually. This study adopts the topic profile of the response from the interviewee as the dialog state representation. In addition, as the response generally consists of several sentences, the summary vector obtained from a long short-term memory neural network (LSTM) is likely to contain noisy information from many irrelevant sentences.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about FINITE-ALPHABET NOMA FOR TWO-USER UPLINK CHANNEL
- Log in to post comments
We consider the non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) design for a classical two-user multiple access channel (MAC) with finite-alphabet inputs. In contrast to the majority of existing NOMA schemes using continuous Gaussian distributed inputs, we consider practical quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) constel- lations at both transmitters, whose sizes are not necessarily the same.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about SOURCE AND DIRECTION OF ARRIVAL ESTIMATION BASED ON MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD COMBINED WITH GMM AND EIGENANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
A method is proposed for estimating the source signal and its direction of arrival (DOA) in this paper. It is based on ML estimation of the transfer function between microphones combined with the EM algorithm for a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM), assuming that the signal is captured at each microphone with delay corresponding to the traveling of sound and some decay. By this modeling, search for the maximum log-likelihood in the ML estimation can be realized simply by eigenvalue decomposition of a properly designed matrix.
ICASSP2018_B0.pdf
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
Sensor selection refers to the problem of intelligently selecting a small subset of a collection of available sensors to reduce the sensing cost while preserving signal acquisition performance. The majority of sensor selection algorithms find the subset of sensors that best recovers an arbitrary signal from a number of linear measurements that is larger than the dimension of the signal.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views
- Read more about Spatiotemporal Attention Based Deep Neural Networks for Emotion Recognition
- Log in to post comments
We propose a spatiotemporal attention based deep neural networks for dimensional emotion recognition in facial videos. To learn the spatiotemporal attention that selectively focuses on emotional sailient parts within facial videos, we formulate the spatiotemporal encoder-decoder network using Convolutional LSTM (ConvLSTM)modules, which can be learned implicitly without any pixel-level annotations. By leveraging the spatiotemporal attention, we also formulate the 3D convolutional neural networks (3D-CNNs) to robustly recognize the dimensional emotion in facial videos.
- Categories:
 83 Views
83 Views
- Read more about SPARSE DISPARITY ESTIMATION USING GLOBAL PHASE ONLY CORRELATION FOR STEREO MATCHING ACCELERATION
- Log in to post comments
In this study, we propose an efficient stereo matching method which estimates sparse disparities using global phase only correlation (POC). Conventionally, cost functions are to be calculated for all disparity candidates and the associated computational cost has been impediment in achieving a real-time performance. Therefore, we consider to use fullimage 2D phase only correlation (FIPOC) for detecting the valid disparity candidates. This will require comparatively fewer calculations for the same number of disparity.
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views
- Read more about End-to-End Multimodal Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
Transcription or sub-titling of open-domain videos is still a chal- lenging domain for Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) due to the data’s challenging acoustics, variable signal processing and the essentially unrestricted domain of the data. In previous work, we have shown that the visual channel – specifically object and scene features – can help to adapt the acoustic model (AM) and language model (LM) of a recognizer, and we are now expanding this work to end-to-end approaches.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
For speech recognition in noisy environments, we propose a multi-task autoencoder which estimates not only clean speech but also noise from noisy speech. We introduce the deSpeeching autoencoder, which excludes speech signals from noisy speech, and combines it with the conventional denoising autoencoder to form a unified multi-task autoencoder (MTAE). We evaluate it using the Aurora 2 data set and 6-hour noise data set collected by ourselves. It reduced WER by 15.7% from the conventional denoising autoencoder in the Aurora 2 test set A.
- Categories:
 125 Views
125 Views