- Image/Video Storage, Retrieval
- Image/Video Processing
- Image/Video Coding
- Image Scanning, Display, and Printing
- Image Formation

- Read more about Deep-URL
- Log in to post comments
The lack of interpretability in current deep learning models causes serious concerns as they are extensively used for various life-critical applications. Hence, it is of paramount importance to develop interpretable deep learning models. In this paper, we consider the problem of blind deconvolution and propose a novel model-aware deep architecture that allows for the recovery of both the blur kernel and the sharp image from the blurred image.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views
- Read more about MULTI IMAGE DEPTH FROM DEFOCUS NETWORK WITH BOUNDARY CUE FOR DUAL APERTURE CAMERA
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we estimate depth information using two defocused images from dual aperture camera. Recent advances in deep learning techniques have increased the accuracy of depth estimation. Besides, methods of using a defocused image in which an object is blurred according to a distance from a camera have been widely studied. We further improve the accuracy of the depth estimation by training the network using two images with different degrees of depth-of-field.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about IMPROVING THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSFORMER BASED LOW RESOURCE SPEECH RECOGNITION FOR INDIAN LANGUAGES
- Log in to post comments
The recent success of the Transformer based sequence-to-sequence framework for various Natural Language Processing tasks has motivated its application to Automatic Speech Recognition. In this work, we explore the application of Transformers on low resource Indian languages in a multilingual framework. We explore various methods to incorporate language information into a multilingual Transformer, i.e.,(i) at the decoder, (ii) at the encoder. These methods include using language identity tokens or providing language information to the acoustic vectors.
shetty.pdf
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
- Read more about INTERPRETABLE SELF-ATTENTION TEMPORAL REASONING FOR DRIVING BEHAVIOR UNDERSTANDING
- Log in to post comments
Performing driving behaviors based on causal reasoning is essential to ensure driving safety. In this work, we investigated how state-of-the-art 3D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) perform on classifying driving behaviors based on causal reasoning. We proposed a perturbation-based visual explanation method to inspect the models' performance visually. By examining the video attention saliency, we found that existing models could not precisely capture the causes (e.g., traffic light) of the specific action (e.g., stopping).
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Parsing Map Guided Multi-Scale Attention Network For Face Hallucination
- Log in to post comments
4929wang.pdf
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about IMAGE SEGMENTATION BASED PRIVACY-PRESERVING HUMAN ACTION RECOGNITION FOR ANOMALY DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
- Read more about COLOUR COMPRESSION OF PLENOPTIC POINT CLOUDS USING RAHT-KLT WITH PRIOR COLOUR CLUSTERING AND SPECULAR/DIFFUSE COMPONENT SEPARATION
- Log in to post comments
The recently introduced plenoptic point cloud representation marries a 3D point cloud with a light field. Instead of each point being associated with a single colour value, there can be multiple values to represent the colour at that point as perceived from different viewpoints. This representation was introduced together with a compression technique for the multi-view colour vectors, which is an extension of the RAHT method for point cloud attribute coding.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views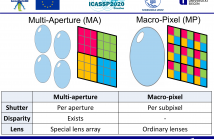
- Read more about Single-Shot Real-Time Multiple-Path Time-of-Flight Depth Imaging for Multi-Aperture and Macro-Pixel Sensors
- Log in to post comments
Multiple-Path Interference (MPI) is a major drawback of Time-of-Flight (ToF) sensors. MPI occurs when a ToF pixel receives more than a single light bounce from the scene. Current methods resolving more than a single return per pixel rely on the sequential acquisition of large amounts of data and are too computationally expensive to deliver depth images in real time. These factors have precluded the development of a multiple-path ToF camera to date. In this work we consider two hardware alternatives that can be used to acquire all necessary raw data in a single shot.
- Categories:
 116 Views
116 Views
- Read more about COMPARE LEARNING: BI-ATTENTION NETWORK FOR FEW-SHOT LEARNING
- Log in to post comments
Learning with few labeled data is a key challenge for visual recognition, as deep neural networks tend to overfit using a few samples only. One of the Few-shot learning methods called metric learning addresses this challenge by first learning a deep distance metric to determine whether a pair of images belong to the same category, then applying the trained metric to instances from other test set with limited labels. This method makes the most of the few samples and limits the overfitting effectively.
- Categories:
 63 Views
63 Views
- Read more about EXPOSURE INTERPOLATION VIA HYBRID LEARNING
- Log in to post comments
Deep learning based methods have become dominant solutions to many image processing problems. A natural question would be “Is there any space for conventional methods on these problems?” In this paper, exposure interpolation is taken as an example to answer this question and the answer is “Yes”. A new hybrid learning framework is introduced to interpolate a medium exposure image for two large-exposure-ratio images from an emerging high dynamic range (HDR) video capturing device. The framework is set up by fusing conventional and deep learning methods.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views