
- Read more about SINGLE IMAGE SUPER-RESOLUTION VIA GLOBAL-CONTEXT ATTENTION NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
In the last few years, single image super-resolution (SISR) has benefited a lot from the rapid development of deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and the introduction of attention mechanisms further improves the performance of SISR. However, previous methods use one or more types of attention independently in multiple stages and ignore the correlations between different layers in the network.
1950_poster.pdf
1950_ICIP21.pdf
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
- Read more about Subband Adaptive Enhancement Of Low Light Images Using Wavelet-Based Convolutional Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
Images captured in low light condition have a narrow dynamic range with a dark tone, which are seriously degraded by noise due to the low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Discrete wavelet transform (DWT) is invertible and thus is able to decompose an image into subbands without information loss minimizing redundancy. In this paper, we propose subband adaptive enhancement of low light images using wavelet-based convolutional neural networks. We adopt DWT to achieve joint contrast enhancement and noise reduction. We combine DWT with convolutional neural networks (CNNs), i.e.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
Tone-mapping is one of the prevailing methods to overcome high dynamic range imaging limitations over low dynamic range display devices, but the tone-mapped output image may suffer from saturated regions with texture and color information loss. In this paper, a novel approach is proposed to solve the so-called clipping problem in tone-mapped high dynamic range images. A successful saturation correction framework, which relies on linear embeddings, difference of pixel intensities and gradient-guided block-search, is developed as a post-processing technique to tone-mapping.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views- Read more about IMAGE FUSION THROUGH LINEAR EMBEDDINGS
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes an effective technique for multi-exposure image fusion and visible-infrared image fusion problems. Multi-exposure fusion algorithms generally extract faulty weight maps when the input stack contains multiple and/or severely over-exposed images. To overcome this issue, an alternative method is developed for weight map characterization and refinement in addition to the perspectives of linear embeddings of images and adaptive morphological masking. This framework has then been extended to the visible and infrared image fusion problem.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Training an Embedded Object Detector for Industrial Settings Without Real Images
- Log in to post comments
In an industrial environment, object detection is a challenging task due to the absence of real images and real-time requirements for the object detector, usually embedded in a mobile device. Using 3D models, it is however possible to create a synthetic dataset to train a neural network, although the performance on real images is limited by the domain gap. In this paper, we study the performance of a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) designed to detect objects in real-time: Single-Shot Detector (SSD) with a MobileNet backbone.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
Erasing text from images is a common image-editing task in film industry and shared media. Existing text-erasing models either tend to produce artifacts or fail to remove all the text in real-world images. In this paper, we follow a two-stage text erasing framework that first masks the text by segmentation, and then inpaints the masked region to create a text-erased image. Our proposed text mask generator is designed to accurately cover text, which combined with inpainting, can produce reliable text-erased results.
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
- Read more about A Fast and Efficient Super-Resolution Network using Hierarchical Dense Residual Learning
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about AN EFFECTIVE SHARPNESS ASSESSMENT METHOD FOR SHALLOW DEPTH-OF-FIELD IMAGES
- Log in to post comments
No-reference (NR) image sharpness assessment is an important issue for image quality assessment and algorithm performance evaluation. Many objective NR sharpness assessment metrics have been proposed which are often intended to be strongly associated with the human visual system (HVS). However, recent studies show that common sharpness assessment indicators may misjudge the degree of blurring for images with shallow depth of field that are often used to highlight the main subject in the view.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
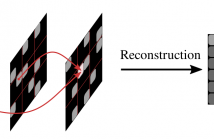
- Read more about Novel Consistency Check For Fast Recursive Reconstruction Of Non-Regularly Sampled Video Data
- Log in to post comments
Quarter sampling is a novel sensor design that allows for an acquisition of higher resolution images without increasing the number of pixels. When being used for video data, one out of four pixels is measured in each frame. Effectively, this leads to a non-regular spatio-temporal sub-sampling. Compared to purely spatial or temporal sub-sampling, this allows for an increased reconstruction quality, as aliasing artifacts can be reduced. For the fast reconstruction of such sensor data with a fixed mask, recursive variant of frequency selective reconstruction (FSR) was proposed.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views