
- Read more about CROSS-LAYER AGGREGATION WITH TRANSFORMERS FOR MULTI-LABEL IMAGE CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
Multi-label image classification task aims to predict multiple object labels in a given image and faces the challenge of variable-sized objects. Limited by the size of CNN convolution kernels, existing CNN-based methods have difficulty
capturing global dependencies and effectively fusing multiple layers features, which is critical for this task. Recently, transformers have utilized multi-head attention to extract feature with long range dependencies. Inspired by this, this
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Generative adversarial network including referring image segmentation for text-guided image manipulation
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a novel generative adversarial network to improve the performance of image manipulation using natural language descriptions that contain desired attributes. Text-guided image manipulation aims to semantically manipulate an image aligned with the text description while preserving text-irrelevant regions. To achieve this, we newly introduce referring image segmentation into the generative adversarial network for image manipulation. The referring image segmentation aims to generate a segmentation mask that extracts the text-relevant region.
- Categories:
 54 Views
54 Views
In this paper, a novel multi-head multi-layer perceptron (MLP) structure is presented for implicit neural representation (INR). Since conventional rectified linear unit (ReLU) networks are shown to exhibit spectral bias towards learning low-frequency features of the signal, we aim at mitigating this defect by taking advantage of local structure of the signals. To be more specific, an MLP is used to capture the global features of the underlying generator function of the desired signal.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about VISION TRANSFORMER EQUIPPED WITH NEURAL RESIZER ON FACIAL EXPRESSION RECOGNITION TASK
- Log in to post comments
When it comes to wild conditions, Facial Expression Recognition is often challenged with low-quality data and imbalanced, ambiguous labels. This field has much benefited from CNN based approaches; however, CNN models have structural limitations to see the facial regions in distance. As a remedy, Transformer has been introduced to vision fields with a global receptive field but requires adjusting input spatial size to the pretrained models to enjoy its strong inductive bias at hands.
1683-1.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about Deep Markov Clustering For Panoptic Segmentation
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views

- Read more about "EFFICIENT UNIVERSAL SHUFFLE ATTACK FOR VISUAL OBJECT TRACKING" Poster
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views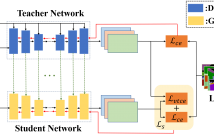
RGB-D semantic segmentation is attracting wide attention due to its better performance than conventional RGB methods. However, most of RGB-D semantic segmentation methods need to acquire the real depth information for segmenting RGB images effectively. Therefore, it is extremely challenging to take full advantage of RGB-D semantic segmentation methods for segmenting RGB images without the depth input.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about Deformable VisTR: Spatio temporal deformable attention for video instance segmentation
- Log in to post comments
Video instance segmentation (VIS) task requires classifying, segmenting, and tracking object instances over all frames in a video clip. Recently, VisTR \cite{vistr} has been proposed as end-to-end transformer-based VIS framework, while demonstrating state-of-the-art performance. However, VisTR is slow to converge during training, requiring around 1000 GPU hours due to the high computational cost of its transformer attention module.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Deep Object Detection With Example Attribute Based Prediction Modulation
- Log in to post comments
Deep object detectors suffer from the gradient contribution imbalance during training. In this paper, we point out that such imbalance can be ascribed to the imbalance in example attributes, e.g., difficulty and shape variation degree. We further propose example attribute based prediction modulation (EAPM) to address it. In EAPM, first, the attribute of an example is defined by the prediction and the corresponding ground truth. Then, a modulating factor w.r.t the example attribute is introduced to modulate the prediction error.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views