
- Read more about DYNAMIC TEXTURE RECOGNITION USING PDV HASHING AND DICTIONARY LEARNING ON MULTI-SCALE VOLUME LOCAL BINARY PATTERN
- Log in to post comments
Spatial-temporal local binary pattern (STLBP) has been widely used in dynamic texture recognition. STLBP often encounters the high-dimension problem as its dimension increases exponentially, so that STLBP could only utilize a small neighborhood. To tackle this problem, we propose a method for dynamic texture recognition using PDV hashing and dictionary learning on multi-scale volume local binary pattern (PHD-MVLBP).
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about SPATIAL-CONTEXT-AWARE DEEP NEURAL NETWORK FOR MULTI-CLASS IMAGE CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about VARIATIONAL BAYESIAN FRAMEWORK FOR ADVANCED IMAGE GENERATION WITH DOMAIN-RELATED VARIABLES
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about VARIATIONAL BAYESIAN FRAMEWORK FOR ADVANCED IMAGE GENERATION WITH DOMAIN-RELATED VARIABLES
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about Model-Based Reconstruction for Collimated Beam Ultrasound Systems
- Log in to post comments
Collimated beam ultrasound systems are a novel technology for imaging inside multi-layered structures such as geothermal wells. Such systems include a transmitter and multiple receivers to capture reflected signals. Common algorithms for ultrasound reconstruction use delay-and-sum (DAS) approaches; these have low computational complexity but produce inaccurate images in the presence of complex structures and specialized geometries such as collimated beams.
ICASSP2022.pdf
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about Adaptive Actor-Critic Bilateral Filter
- Log in to post comments
Recent research on edge-preserving image smoothing has suggested that bilateral filtering is vulnerable to maliciously perturbed filtering input. However, while most prior works analyze the adaptation of the range kernel in one-step manner, in this paper we take a more constructive view towards multi-step framework with the goal of unveiling the vulnerability of bilateral filtering.
Paper1162_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 59 Views
59 Views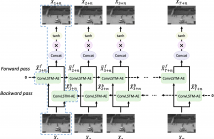
- Read more about Video Anomaly Detection via Prediction Network with Enhanced Spatio-temporal Memory Exchange
- Log in to post comments
Video anomaly detection is a challenging task because most anomalies are scarce and non-deterministic. Many approaches investigate the reconstruction difference between normal and abnormal patterns, but neglect that anomalies do not necessarily correspond to large reconstruction errors. To address this issue, we design a Convolutional LSTM Auto-Encoder prediction framework with enhanced spatio-temporal memory exchange using bi-directionalilty and a higher-order mechanism. The bi-directional structure promotes learning the temporal regularity through forward and backward predictions.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Read more about LOOK, LISTEN AND PAY MORE ATTENTION: FUSING MULTI-MODAL INFORMATION FOR VIDEO VIOLENCE DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
Violence detection is an essential and challenging problem in the computer vision community. Most existing works focus on single modal data analysis, which is not effective when multi-modality is available.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
Few-shot segmentation has got a lot of concerns recently. Existing methods mainly locate and recognize the target object based on a cross-guided way that applies masked target object features of sup- port(query) images to make a feature matching with query(support) images. However, there are some differences between support images and query images because of large appearance and scale variation, which will lead to inaccurate and incomplete segmentation. This problem inspired us to explore the local coherence of the image to guide the segmentation.
icassp.pptx
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Learning task-specific representation for Video anomaly detection with spatial-temporal attention
- Log in to post comments
The automatic detection of abnormal events in surveillance videos with weak supervision has been formulated as a multiple instance learning task, which aims to localize the clips containing abnormal events temporally with the video-level labels. However, most existing methods rely on the features extracted by the pre-trained action recognition models, which are not discriminative enough for video anomaly detection.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views