
- Read more about PHONEME BOUNDARY DETECTION USING LEARNABLE SEGMENTAL FEATURES
- Log in to post comments
Phoneme boundary detection plays an essential first step for a variety of speech processing applications such as speaker diarization, speech science, keyword spotting, etc. In this work, we propose a neural architecture coupled with a parameterized structured loss function to learn segmental representations for the task of phoneme boundary detection. First, we evaluated our model when the spoken phonemes were not given as input.
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views
- Read more about Semi-Supervised Optimal Transport Methods for Detecting Anomalies
- Log in to post comments
Building upon advances on optimal transport and anomaly detection, we propose a generalization of an unsupervised and automatic method for detection of significant deviation from reference signals. Unlike most existing approaches for anomaly detection, our method is built on a non-parametric framework exploiting the optimal transportation to estimate deviation from an observed distribution.
- Categories:
 54 Views
54 Views
- Read more about UNIFIED SIGNAL COMPRESSION USING GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
We propose a unified compression framework that uses generative adversarial networks (GAN) to compress image and speech signals. The compressed signal is represented by a latent vector fed into a generator network which is trained to produce high-quality signals that minimize a target objective function. To efficiently quantize the compressed signal, non-uniformly quantized optimal latent vectors are identified by iterative back-propagation with ADMM optimization performed for each iteration.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about LOW MUTUAL AND AVERAGE COHERENCE DICTIONARY LEARNING USING CONVEX APPROXIMATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Multi-step Online Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we address the Online Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (OUDA) problem, where the target data are unlabelled and arriving sequentially. The traditional methods on the OUDA problem mainly focus on transforming each arriving target data to the source domain, and they do not sufficiently consider the temporal coherency and accumulative statistics among the arriving target data. We propose a multi-step framework for the OUDA problem, which institutes a novel method to compute the mean-target subspace inspired by the geometrical interpretation on the Euclidean space.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views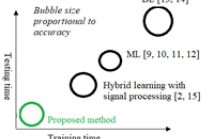
- Read more about INSTANT ADAPTIVE LEARNING: AN ADAPTIVE FILTER BASED FAST LEARNING MODEL CONSTRUCTION FOR SENSOR SIGNAL TIME SERIES CLASSIFICATION ON EDGE DEVICES
- Log in to post comments
Construction of learning model under computational and energy constraints, particularly in highly limited training time requirement is a critical as well as unique necessity of many practical IoT applications that use time series sensor signal analytics for edge devices. Yet, majority of the state-of-the-art algorithms and solutions attempt to achieve high performance objective (like test accuracy) irrespective of the computational constraints of real-life applications.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about Detect insider attacks using CNN in Decentralized Optimization
- Log in to post comments
This paper studies the security issue of a gossip-based distributed projected gradient (DPG) algorithm, when it is applied for solving a decentralized multi-agent optimization. It is known that the gossip-based DPG algorithm is vulnerable to insider attacks because each agent locally estimates its (sub)gradient without any supervision. This work leverages the convolutional neural network (CNN) to perform the detection and localization of the insider attackers.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Reconstruction of FRI Signals Using Deep Neural Network Approaches
- Log in to post comments
Finite Rate of Innovation (FRI) theory considers sampling and reconstruction of classes of non-bandlimited continuous signals that have a small number of free parameters, such as a stream of Diracs. The task of reconstructing FRI signals from discrete samples is often transformed into a spectral estimation problem and solved using Prony's method and matrix pencil method which involve estimating signal subspaces. They achieve an optimal performance given by the Cramér-Rao bound yet break down at a certain peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR).
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Learning to Estimate Driver Drowsiness from Car Acceleration Sensors using Weakly Labeled Data
- Log in to post comments
This paper addresses the learning task of estimating driver drowsiness from the signals of car acceleration sensors. Since even drivers themselves cannot perceive their own drowsiness in a timely manner unless they use burdensome invasive sensors, obtaining labeled training data for each timestamp is not a realistic goal. To deal with this difficulty, we formulate the task as a weakly supervised learning. We only need to add labels for each complete trip, not for every timestamp independently.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about CONFIRMNET: CONVOLUTIONAL FIRMNET AND APPLICATION TO IMAGE DENOISING AND INPAINTING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views