Documents
Presentation Slides
CNN-BASED ACTION RECOGNITION USING ADAPTIVE MULTISCALE DEPTH MOTION MAPS AND STABLE JOINT DISTANCE MAPS
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Junyou He
- Last updated:
- 20 November 2018 - 5:44am
- Document Type:
- Presentation Slides
- Document Year:
- 2018
- Event:
- Paper Code:
- 1466
- Categories:
- Log in to post comments
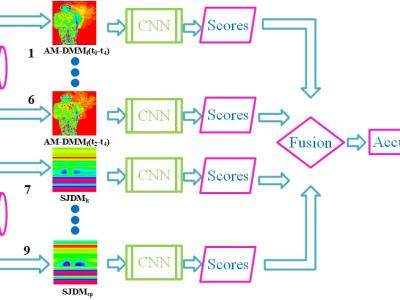
Human action recognition has a wide range of applications including biometrics and surveillance. Existing methods mostly focus on a single modality, insufficient to characterize variations among different motions. To address this problem, we present a CNN-based human action recognition framework by fusing depth and skeleton modalities. The proposed Adaptive Multiscale Depth Motion Maps (AM-DMMs) are calculated from depth maps to capture shape, motion cues. Moreover, adaptive temporal windows ensure that AM-DMMs are robust to motion speed variations. A compact and effective method is also proposed to encode the spatio-temporal information of each skeleton sequence into three maps, referred to as Stable Joint Distance Maps (SJDMs) which describe different spatial relationships between the joints. A multi-channel CNN is adopted to exploit the discriminative features from texture color images encoded from AM-DMMs and SJDMs for effective recognition. The proposed method has been evaluated on UTD-MHAD Dataset and achieves the state-of-the-art result.

