- Read more about Supplemental_FFGLC
- Log in to post comments
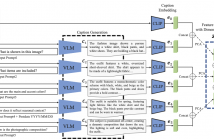
This supplementary material provides a comprehensive overview of the implementation details and evaluation of FFGLC, our proposed method for fashion social media popularity prediction. To enhance reproducibility, the implementation section includes detailed prompts used for generating captions, descriptions of the newly constructed WEAR-PD dataset, the integration process of FFGLC into existing popularity prediction frameworks, and specifications of hyperparameters and computational resources. In the evaluation section, both quantitative and qualitative analyses are presented.
- Categories:
 77 Views
77 Views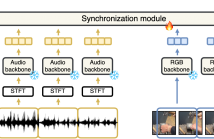
- Read more about Poster: Synchformer: Efficient Synchronization from Sparse Cues
- Log in to post comments
Our objective is audio-visual synchronization with a focus on ‘in-the-wild’ videos, such as those on YouTube, where synchronization cues can be sparse. Our contributions include a novel audio-visual synchronization model, and training that decouples feature extraction from synchronization modelling through multi-modal segment-level contrastive pre-training. This approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in both dense and sparse settings.
vi_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
- Read more about UNIFIED PRETRAINING TARGET BASED CROSS-MODAL VIDEO-MUSIC RETRIEVAL
- Log in to post comments
Background music (BGM) can enhance the video’s emotion and thus make it engaging. However, selecting an appropriate BGM often requires domain knowledge or a deep understanding of the video. This has led to the development of video-music retrieval techniques. Most existing approaches utilize pre-trained video/music feature extractors trained with different target sets to obtain average video/music-level embeddings for cross-modal matching. The drawbacks are two-fold. One is that different target sets for video/music pre-training may cause the generated embeddings difficult to match.
icassp-cbv.pdf
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Exploring Latent Cross-Channel Embedding for Accurate 3D Human Pose Reconstruction in a Diffusion Framework
- Log in to post comments
Monocular 3D human pose estimation poses significant challenges due to the inherent depth ambiguities that arise during the reprojection process from 2D to 3D. Conventional approaches that rely on estimating an over-fit projection matrix struggle to effectively address these challenges and often result in noisy outputs. Recent advancements in diffusion models have shown promise in incorporating structural priors to address reprojection ambiguities.
- Categories:
 54 Views
54 Views
- Read more about Character Attribute Extraction from Movie Scripts using LLMs
- Log in to post comments
Narrative understanding is an integrative task of studying characters, plots, events, and relations in a story.
It involves natural language processing tasks such as named entity recognition and coreference resolution to identify the characters, semantic role labeling and argument mining to find character actions and events, information extraction and question answering to describe character attributes, causal analysis to relate different events, and summarization to find the main storyline.
- Categories:
 94 Views
94 Views
- Read more about PROMPTING LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS WITH FINE-GRAINED VISUAL RELATIONS FROM SCENE GRAPH FOR VISUAL QUESTION ANSWERING
- Log in to post comments
Visual Question Answering (VQA) is a task that requires models to comprehend both questions and images. An increasing number of works are leveraging the strong reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) to address VQA. These methods typically utilize image captions as visual text description to aid LLMs in comprehending images. However, these captions often overlooking the relations of fine-grained objects, which will limit the reasoning capability of LLMs. In this paper, we present PFVR, a modular framework that Prompts LLMs with Fine-grained Visual Relationships for VQA.
- Categories:
 66 Views
66 Views
- Read more about SMALL OBJECT DETECTION ON THE WATER SURFACE BASED ON RADAR AND CAMERA FUSION
- Log in to post comments
With the growing applications of water operations, water surface object detection tasks are facing new challenges. In this paper, we focus on improving the performance of water surface small object detection. Due to the limitations of single sensor in water environments, we propose RCFNet, a novel small object detection method based on radar-vision fusion. RCFNet fuses features captured by radar and camera in multiple stages to generate more effective target feature representations for small object detection on water surfaces.
- Categories:
 67 Views
67 Views
- Read more about A Joint Model-Driven Unfolding Network For Degraded Low-Quality Color-Depth Images Enhancement
- Log in to post comments
Inspired by multi-task learning, degraded low-quality color-depth images enhancement tasks are transformed as a joint color-depth optimization model by using maximum a posteriori estimation. This model is optimized alternatively in an iterative way to get the solutions of CGD-SR task and Low-Brightness Color Image Enhancement (LBC-IE) task. The whole iterative optimization procedure is expanded as a joint model-driven unfolding network.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about ASYMMETRIC SCALABLE CROSS-MODAL HASHING
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
pre_icip.pdf
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views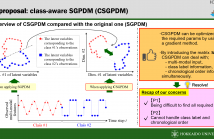
- Read more about Class-aware Shared Gaussian Process Dynamic Model
- Log in to post comments
A new method of Gaussian process dynamic model (GPDM), named class-aware shared GPDM (CSGPDM), is presented in this paper. One of the most difference between our CSGPDM and existing GPDM is considering class information which helps to build the class label-based latent space being effective for the following class-related tasks. In terms of representation learning, CSGPDM is optimized by considering not only a non-linear relationship but also time-series relation and discriminative information of each class label.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views