Documents
Poster
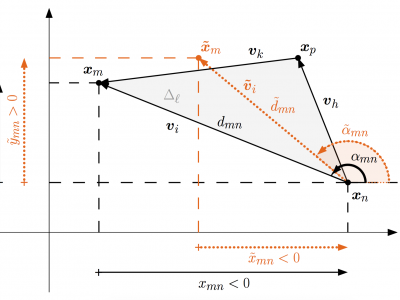
Combining range and direction for improved localization
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Miranda Krekovic
- Last updated:
- 13 April 2018 - 5:37am
- Document Type:
- Poster
- Document Year:
- 2018
- Event:
- Presenters:
- Miranda Krekovic
- Paper Code:
- SAM-P5
- Categories:
- Keywords:
- Log in to post comments
Self-localization of nodes in a sensor network is typically achieved using either range or direction measurements; in this paper, we show that a constructive combination of both improves the estimation. We propose two localization algorithms that make use of the differences between the sensors’ coordinates, or edge vectors; these can be calculated from measured distances and angles. Our first method improves the existing edge-multidimensional scaling algorithm (E-MDS) by introducing additional constraints
that enforce geometric consistency between the edge vectors. On the other hand, our second method decomposes the edge vectors onto 1-dimensional spaces and introduces the concept of coordinate difference matrices (CDMs) to independently regularize each projection. This solution is optimal when Gaussian noise is added to the edge vectors. We demonstrate in numerical simulations that both algorithms outperform state-of-the-art solutions.

