Documents
Poster
QUALITY CONTROL OF VOICE RECORDINGS IN REMOTE PARKINSON'S DISEASE MONITORING USING THE INFINITE HIDDEN MARKOV MODEL
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Amir Hossein Poorjam
- Last updated:
- 12 May 2019 - 6:13pm
- Document Type:
- Poster
- Document Year:
- 2019
- Event:
- Presenters:
- Amir H. Poorjam
- Paper Code:
- 3179
- Categories:
- Keywords:
- Log in to post comments
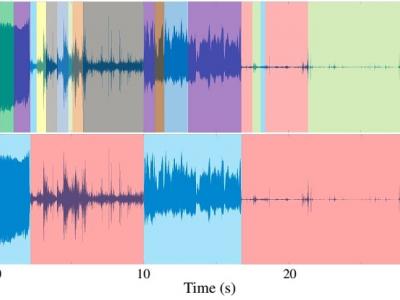
The performance of voice-based systems for remote monitoring of Parkinson’s disease is highly dependent on the degree of adherence of the recordings to the test protocols, which probe for specific symptoms. Identifying segments of the signal that adhere to the protocol assumptions is typically performed manually by experts. This process is costly, time consuming, and often infeasible for large-scale data sets. In this paper, we propose a method to automatically identify the segments of signals that violate the test protocol with a high accuracy. In our approach, the signal is first split into variable duration segments by fitting an infinite hidden Markov model (iHMM) to the frames of the signals in the mel-frequency cepstral domain. The complexity of the iHMM is capable of growing jointly with the data allowing us to infer a potentially large (asymptotically infinite) number of different phenomena segmented into different hidden states. Then, we identify the segments that adhere to the test protocol by applying a multinomial naive Bayes classifier to the state indicators of segments. The experimental results show that even by using a small amount of training data, we can achieve around 96% accuracy in identifying short-term protocol violations with a 0.2 s resolution.

