
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.

In this research project, we are interested by finding solutions to the problem of image analysis and processing in the encrypted domain. For security reasons, more and more digital data are transferred or stored in the encrypted domain. However, during the transmission or the archiving of encrypted images, it is often necessary to analyze or process them, without knowing the original content or the secret key used during the encryption phase. We propose to work on this problem, by associating theoretical aspects with numerous applications.
- Categories:
 160 Views
160 Views
- Read more about HIGH THROUGHPUT BLOCK CODING IN THE HTJ2K COMPRESSION STANDARD
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
This paper describes the block coding algorithm that underpins the new High Throughput JPEG 2000 (HTJ2K) standard. The objective of HTJ2K is to overcome the computational complexity of the original block coding algorithm, by providing a drop-in replacement that preserves as much of the JPEG 2000 feature set as possible, while allowing reversible transcoding to/from the original format. We show how the new standard achieves these goals, with high coding efficiency, and extremely high throughput in software.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
- Read more about Privacy Protection for Social Media based on a Hierarchical Secret Image Sharing Scheme
- Log in to post comments
Social network development raises many issues relating to privacy protection for images. In particular, multi-party privacy protection conflicts can take place when an image is published by only one of its owners. Indeed, privacy settings applied to this image are those of its owner and people on the image are not involved in the process. In this paper, we propose a new hierarchical secret image sharing scheme for social networks in order to answer this problem.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views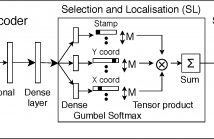
Unsupervised object discovery in images involves uncovering recurring patterns that define objects and discriminates them against the background. This is more challenging than image clustering as the size and the location of the objects are not known: this adds additional degrees of freedom and increases the problem complexity. In this work, we propose StampNet, a novel autoencoding neural network that localizes shapes (objects) over a simple background in images and categorizes them simultaneously.
StampNet.pdf
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Partition Tree Guided Progressive Rethinking Network for in-Loop Filtering of HEVC
- Log in to post comments
In-Loop filter is a key part in High Efficiency Video Coding(HEVC) which effectively removes the compression artifacts.Recently, many newly proposed methods combine residual learning and dense connection to construct a deeper network for better in-loop filtering performance. However,the long-term dependency between blocks is neglected, and information usually passes between blocks only after dimension compression.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
This paper presents a framework for accurately tracking objects of complex shapes with joint minimization of geometric and photometric parameters using a coarse 3D object model with the RGB-D cameras. Tracking with coarse 3D model is remarkably useful for industrial applications. A technique is proposed that uses a combination of point-to-plane distance minimization and photometric error minimization to track objects accurately. The concept of 'keyframes' are used in this system of object tracking for minimizing drift.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views- Read more about A Metrological Measurement of Texture in Hyperspectral Images using Relocated Spectral Difference Occurrence Matrix
- Log in to post comments
A new hyperspectral texture descriptor, Relocated Spectral Difference Occurrence Matrix (rSDOM) is proposed. It assesses the distribution of spectral difference in a given neighborhood. For metrological purposes, rSDOM employs Kullback-Leibler pseudo-divergence (KLPD) for spectral difference calculation. It is generic and adapted for any spectral range and number of band. As validation, a texture classification scheme based on nearest neighbor classifier is applied on HyTexiLa dataset using rSDOM.
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views
- Read more about Dual reverse attention networks for person re-identification
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we enhance feature representation ability of person re-identification (Re-ID) by learning invariances to hard examples. Unlike previous works of hard examples mining and generating in image level, we propose a dual reverse attention network (DRANet) to generate hard examples in the convolutional feature space. Specifically, we use a classification branch of attention mechanism to model that ‘what’ in channel and ‘where’ in spatial dimensions are informative in the feature maps.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Spatially Regularized Multi-exponential Transverse Relaxation Times Estimation from Magnitude Magnetic Resonance Images Under Rician Noise
- Log in to post comments
The extraction of multi-exponential decay parameters from multi-temporal images corrupted with Rician noise and with limited time samples proves to be a challenging problem frequently encountered in clinical and food MRI studies. This work aims at proposing a method for the estimation of multiexponential transverse relaxation times from noisy magnitude MRI images. A spatially regularized Maximum-Likelihood estimator accounting for the Rician distribution of the noise is introduced.
ICIP_1976.pdf
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views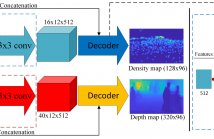
- Read more about DANET: DEPTH-AWARE NETWORK FOR CROWD COUNTING
- Log in to post comments
Image-based people counting is a challenging work due to the large scale variation problem caused by the diversity of distance between the camera and the person, especially in the congested scenes. To handle this problem, the previous methods focus on building complicated models and rely on labeling the sophisticated density maps to learn the scale variation implicitly. It is often time-consuming in data pre-processing and difficult to train these deep models due to the lack of training data.
- Categories:
 56 Views
56 Views