
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.

This paper proposes an approach to automatically categorize the social interactions of a user wearing a photo-camera (2fpm), by relying solely on what the camera is seeing. The problem is challenging due to the overwhelming complexity of social life and the extreme intra-class variability of social interactions captured under unconstrained conditions. We adopt the formalization proposed in Bugental’s social theory, that groups human relations into five social domains with related categories.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about Long & Short Memory Balancing In Visual Co-tracking using Q-learning
- Log in to post comments
Employing one or more additional classifiers to break the self-learning loop in tracing-by-detection has gained considerable attention. Most of such trackers merely utilize the redundancy to address the accumulating label error in the tracking loop, and suffer from high computational complexity as well as tracking challenges that may interrupt all classifiers (e.g. temporal occlusions). We propose the active co-tracking framework, in which the main classifier of the tracker labels samples of the video sequence, and only consults auxiliary classifier when it is uncertain.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about A NOVEL BLIND IMAGE QUALITY ASSESSMENT METHOD BASED ON REFINED NATURAL SCENE STATISTICS
- Log in to post comments
Natural scene statistics (NSS) model has received considerable attention in the image quality assessment (IQA) community due to its high sensitivity to image distortion. However, most existing NSS-based IQA methods extract features either from spatial domain or from transform domain. There is little work to simultaneously consider the features from these two domains. In this paper, a novel blind IQA method (NBIQA) based on refined NSS is proposed. The proposed NBIQA first investigates the performance of a large number of candidate features from both the spatial and transform domains.
- Categories:
 103 Views
103 Views
- Read more about Adaptive Hard Example Mining for Image Captioning
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about AN END-TO-END MULTI-SCALE RESIDUAL RECONSTRUCTION NETWORK FOR IMAGE COMPRESSIVE SENSING
- Log in to post comments
Recently, deep-learning based reconstruction models have been proposed to improve recovery performance of compressive sensed image and overcome expensive time complexity drawbacks of iteration-based traditional algorithms. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end multi-scale residual convolutional neural network (CNN), dubbed MSRNet, to simulate image compressive sensing (CS) and inverse reconstruction process in real situation. In MSRNet, we apply three parallel channels with different convolution kernel sizes to exploit different-scale feature information.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views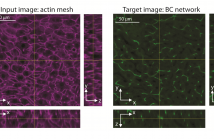
- Read more about PREDICTION OF MULTIPLE 3D TISSUE STRUCTURES BASED ON SINGLE-MARKER IMAGES USING CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
A quantitative understanding of complex biological systems such as tissues requires reconstructing the structure of the different components of the system. Fluorescence microscopy provides the means to visualize simultaneously several tissue components. However, it can be time consuming and is limited by the number of fluorescent markers that can be used. In this study, we describe a toolbox of algorithms based on convolutional neural networks for the prediction of 3D tissue structures by learning features embedded within single-marker images.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views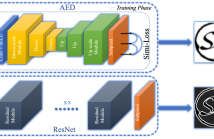
- Read more about PRED: A PARALLEL NETWORK FOR HANDLING MULTIPLE DEGRADATIONS VIA SINGLE MODEL IN SINGLE IMAGE SUPER-RESOLUTION
- Log in to post comments
Existing SISR (single image super-resolution) methods mostly assume that a low-resolution (LR) image is bicubicly downsampled from its high-resolution (HR) counterpart, which inevitably give rise to poor performance when the degradation is out of assumption. To address this issue, we propose a framework PRED (parallel residual and encoder-decoder network) with an innovative training strategy to enhance the robustness to multiple degradations. Consequently, the network can handle spatially variant degradations, which significantly improves the practicability of the proposed method.
poster.pptx
PRED_paper.pdf
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about FEATURE EXTRACTION AND TRACKING OF CNN SEGMENTATIONS FOR IMPROVED ROAD DETECTION FROM SATELLITE IMAGERY
- Log in to post comments
Road detection in high-resolution satellite images is an important and popular research topic in the field of image processing. In this paper, we propose a novel road extraction and tracking method based on road segmentation results from a convolutional network, providing improved road detection. The proposed method incorporates our previously proposed connected-tube marked point process (MPP) model and a post-tracking algorithm. We present experimental results on the Massachusetts roads dataset to show the performance of our method on road detection in remotely-sensed images.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about TAKING ME TO THE CORRECT PLACE: VISION-BASED LOCALIZATION FOR AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Vehicle localization is a critical component for autonomous driving, which estimates the position and orientation of vehicles. To achieve the goal of quick and accurate localization, we develop a system that can dynamically switch the features applied for localization. Specifically, we develop a feature based on convolutional neural network targeting at accurate matching, which proves high rotation invariant property that can help to overcome the relatively large error when vehicles turning at corners.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about FAST AND LIGHTWEIGHT IMAGE SUPER-RESOLUTION BASED ON DENSE RESIDUALS TWO-CHANNEL NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
The existing advanced super-resolution methods with deepening or widening network demand high computational resources and memory consumption. It is difficult to directly apply them in practice. Therefore, we propose a fast and lightweight two-channel end-to-end network with fewer parameters and low computational complexity in this paper. The shallow channel mainly restores the general outline of the image, while the deep channel mainly learns the high- frequency texture information. And the deep channel combines the dense block and residual connection.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views