- Signal and System Modeling, Representation and Estimation
- Multirate Signal Processing
- Sampling and Reconstruction
- Nonlinear Systems and Signal Processing
- Filter Design
- Adaptive Signal Processing
- Statistical Signal Processing

- Read more about LARGE SCALE RANDOMIZED LEARNING GUIDED BY PHYSICAL LAWS WITH APPLICATIONS IN FULL WAVEFORM INVERSION
- Log in to post comments
The rapid convergence rate, high fidelity learning outcome and low computational cost are key targets in solving the learning problem of the complex physical system. Guided
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views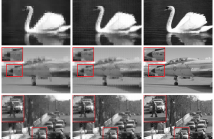
- Read more about Designing Constrained Projections for Compressed Sensing: Mean Errors and Anomalies with Coherence
- Log in to post comments
Most existing work in designing sensing matrices for compressive recovery is based on optimizing some quality factor, such as mutual coherence, average coherence or the restricted isometry constant (RIC), of the sensing matrix. In this paper, we report anomalous results that show that such a design is not always guaranteed to improve reconstruction results.
- Categories:
 73 Views
73 Views
- Read more about A Multicore Convex Optimization Algorithm with Applications to Video Restoration
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present a new distributed algorithm for minimizing a sum of non-necessarily differentiable convex
functions composed with arbitrary linear operators. The overall cost function is assumed strongly convex.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about SAVE - Space Alternating Variational Estimation for Sparse Bayesian Learning
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Data-Driven Nonparametric Hypothesis Testing
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Hi, BCD! Hybrid Inexact Block Coordinate Descent for Hyperspectral Super-Resolution
- Log in to post comments
Hyperspectral super-resolution (HSR) is a problem of recovering a high-spectral-spatial-resolution image from a multispectral measurement and a hyperspectral measurement, which have low spectral and spatial resolutions, respectively. We consider a low-rank structured matrix factorization formulation for HSR, which is a non-convex large-scale optimization problem. Our contributions contain both computational and theoretical aspects.
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views
- Read more about EFFICIENT CONVOLUTIONAL DICTIONARY LEARNING USING PARTIAL UPDATE FAST ITERATIVE SHRINKAGE-THRESHOLDING ALGORITHM
- Log in to post comments
Convolutional sparse representations allow modeling an entire image as an alternative to the more common independent patch-based
formulations. Although many approaches have been proposed to efficiently solve the convolutional dictionary learning (CDL) problem,
their computational performance is constrained by the dictionary update stage. In this work, we include two improvements to existing
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Robust PCA via Dictionary Based Outlier Pursuit
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about Probability Reweighting in Social Learning: Optimality and Suboptimality
- Log in to post comments
This work explores sequential Bayesian binary hypothesis testing in the social learning setup under expertise diversity. We consider a two-agent (say advisor-learner) sequential binary hypothesis test where the learner infers the hypothesis based on the decision of the advisor, a prior private signal, and individual belief. In addition, the agents have varying expertise, in terms of the noise variance in the private signal.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views